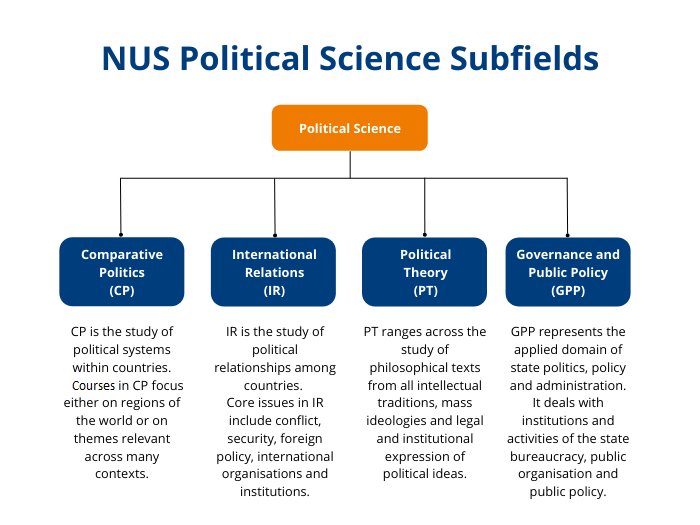
Course Listing by Subfields

-
Note: Level 6000 courses cannot be read towards the B.A / B.Soc Sci Honours Requirements.
-
Note that these courses will only be offered to Cohort 2014 and earlier.
- GEK1003
- GEK2024
- GEK2010
- GEK2012
- SSA2222
- GEK2003
- SSA2209
- GEK2025
- GEK2043
- SSA3205
- GEK3005
- GEK3006
- GEK3007
GES1034/ GESS1024 - We the Citizens - Understanding Singapore's Politics
Units: 4
Pre-requisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): Nil
The course initiates students into the workings of politics from the perspective of citizenship. What constitutes citizenship? What are the roles, duties and obligations of being a Singapore citizen? How do citizens interact and impact politics and decision making in Singapore? How have changes over the years, including (a) perspective of Singapore’s political history, (b) imperatives shaping national politics, (c) the political system, (d) its key structures and approaches to nation building, affected national politics and in turn, led to the political elites responding to changing demands of citizens? The role of civic and civil society will also be discussed.
PS1101E - Introduction to Politics
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): GEM1003K, GEK1003, PS1101
The purpose of this module is to impart a preliminary overview of political science and its sub-fields so that students have a basic orientation of the discipline. It briefly explains the scope and components of each of the four sub-fields (political theory, comparative politics, international relations and public administration) and familiarises students with the major issues and arguments related to power, justice, political culture, national identity, accountability, ethics and world order. It also focuses on key political institutions. The module will be of interest to students across the university who want to gain a basic understanding of politics.
PS3257 - Political Inquiry
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Completed 12 units in Political Science or 16 units in GL or GL-recognised non-language modules.
Preclusion(s): PS2102, PS2102B, PS2231B
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module examines the theories of knowledge and methods of inquiry appropriate to studying politics. It introduces students to alternative understandings of the social sciences and to the empirical, critical, and analytical skills they imply. It pays particular attention to helping students understand the basics of good research and to acquire skills essential to conducting their own research.
PS3258 - Research Methods in Political Science
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): PS3257
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module provides a survey of different methodological approaches to the study of political science: single case studies, qualitative comparative analysis, and a variety of quantitative methods. The module focuses more on applications than theories, and explains how political questions can be investigated using different types of data and methods. All students are expected to have completed PS3257 (Political Inquiry) or an equivalent introductory research methodology module. Students are required to work on group research projects and present their findings at the end of the semester.
PS3880G - Research Design and Methods
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): PS3257
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
The module provides undergraduate students with intensive, focused, and hands-on training in specific research methods. It introduces students to and familiarizes them with such quantitative and qualitative methods as multiple regression, qualitative comparative analysis, experimental design, and interpretative methods. While the existing modules PS3257: Political Inquiry and PS3258: Research Methods in Political Science provide undergraduates with a broad overview of all the many different methods and methodological approaches, the module aims to teach them the detailed ins and outs of one specific research method used by political scientists and researchers in neighboring social science disciplines.
PS4314 - Data Analytics in Political Science
Units: 5
Prerequisite(s): Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS or 28 Units in GL/GL recognised non-language modules, with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track, and PS3257 Political Inquiry
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
Data analytics is an increasingly essential skill for political science research. This module teaches a range of analytical tools in data analysis and statistics to understand important and interesting questions about politics, societies and human behaviour. It covers data analysis concepts such as causality, measurement, prediction, probability, and statistical tools. It provides hands-on instruction using R programming and datasets from leading quantitative social science research.
PS5111R - Research Design in Political Science
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): PS5101, PS6101
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module is an introduction to some of the research methods used in the empirical study of politics and public policy. The objective is to familiarise students with (i) concepts in research design, and (ii) practices in analytical methods. Topics covered include the logic of empirical research, sampling methods, descriptive statistics, probability distributions, statistical estimation and inference, and hypothesis testing in group comparisons and regression analysis. Besides regular homework assignments, there will also be a mid-term test, a project, and a final examination.
PS5602R - Introduction to Quantitative Methods
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module covers basic inferential statistics and its application to the systematic study of politics. Topics covered will include descriptive statistics, sampling and probability, simple and multiple regression, interpretation of regression coefficients, regression diagnostics, visualisation of data, and computation of quantities of substantive interest. The focus is on the statistical underpinnings of the ordinary least square regression model and on developing practical data analysis skills.
PS5603R - Introduction to Qualitative Methods
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module is an introduction to qualitative methods in political science. After a review of the main competing epistemological approaches we concentrate on the most prevalent qualitative method in political science: the comparative case-study. We then turn to interpretivism, ethnography, and discourse analysis, and their respective applications in political science.
PS6603 - Topics in Research Methods
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): PS5111
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
The module provides graduate students with intensive, focused, and hands-on training in specific advanced research methods. It introduces students to and familiarizes them with such advanced quantitative and qualitative methods as multiple regression, structural equation modeling, qualitative comparative analysis, experimental design, and interpretative methods. Unlike existing methods modules, which aim to provide a general introduction to a wide variety of research methods, this module focuses on the development of highly specific methodological skills.
PS3550 - Political Science Internship
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Students should: (i) have completed a minimum of 24 units in Political Science and (ii) have declared Political Science as their Major.
Preclusion(s): Any other XX3550 internship modules.
(Note: Students who change majors may not do a second internship in their new major).
Cross-listing(s): Nil
Internships vary in length but all take place within an organisation, are vetted and approved by the Department’s internship advisor, have relevance to the major in Political Science, involve the application of subject knowledge and theory in reflection upon the work, and are assessed. Available credited internships (if any) will be advertised at the beginning of each semester. In exceptional cases, internships proposed by students may be approved by the Department.
IPS3550 - Extended Political Science Internship
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Students should: (i) have completed a minimum of 24 units in Political Science and (ii) have declared Political Science as their Major.
Preclusion(s): Any other XX3550 internship modules.
(Note: Students who change majors may not do a second internship in their new major).
Cross-listing(s): Nil
Internships vary in length but all take place within an organisation, are vetted and approved by the Department’s internship advisor, have relevance to the major in Political Science, involve the application of subject knowledge and theory in reflection upon the work, and are assessed. Available credited internships (if any) will be advertised at the beginning of each semester. In exceptional cases, internships proposed by students may be approved by the Department.
PS3551 - FASS Undergraduate Research Opportunity (UROP)
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Students must have declared a Major, completed a minimum of 24 Units in that Major, and have a GPA of at least 3.5
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
A UROP involves the student working with a supervisor, and usually in a team, on an existing research project. It has relevance to the student’s Major, and involves the application of subject knowledge, methodology and theory in reflection upon the research project.
UROPs usually take place within FASS or ARI, though a few involve international partners. All are vetted and approved by the Major department. All are assessed. UROPs can be proposed by supervisor or student, and require the approval of the Major department.
PS4401 - Honours Thesis
Units: 15
Prerequisite(s): Cohort 2015 and before: Completed 110 units, including 60 units of PS major requirements with a minimum SJAP of 4.00 and GPA of 3.50. Students may seek a waiver of the SJAP pre-requisite from the department if they have a minimum GPA of 4.25 after completing 110 units.
Cohort 2016 onwards: Completed 110 units, including 44 units of PS major requirements with a minimum SJAP of 4.00 and GPA of 3.50. Students may seek a waiver of the SJAP pre-requisite from the department if they have a minimum GPA of 4.25 after completing 110 units.
Preclusion(s): PS4660
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This is basically a research and writing exercise to be supervised by a member of the Department staff. Those who qualify are expected to select a research topic in any subfield of Political Science, conduct research on the topic, collect and analyse data, present arguments, complete the thesis, and submit it within the stipulated deadline. The length of the thesis should not exceed 10,000 words. Each thesis is assessed by two examiners (including the supervisor), and it is meant only for Honours Year students in Political Science.
Please register PS4401 manually with the Department.
PS4660 - Independent Study
Units: 5
Prerequisite(s):
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 100 units, including 60 units in PS with a minimum GPA of 3.50.
Cohort 2012 onwards:
Completed 100 units, including 60 units in PS with a minimum GPA of 3.20.
Preclusion(s): PS4401, PS4401S
Cross-listing(s): Nil
The Independent Study Module is designed to enable the student to explore an approved topic within the discipline in depth. The student should approach a lecturer to work out an agreed topic, readings, and assignments for the module. Regular meetings and reports are expected. Evaluation is based on 100% Continuous Assessment and must be worked out between the student and the lecturer prior to seeking departmental approval.
Please register PS4660 manually with the Department.
PS6660 - Independent Study
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
Independent research plays an important role in graduate education. The Independent Study Module is designed to enable the student to explore an approved topic in Political Science in depth. The student should approach a lecturer to work out an agreed topic, readings, and assignments for the module. A formal, written agreement is to be drawn up, giving a clear account of the topic, programme of study, assignments, evaluation, and other pertinent details. The Head’s and/or Graduate Coordinator’s approval of the written agreement is required. Regular meetings and reports are expected. Evaluation is based on 100% Continuous Assessment and must be worked out between the student and the lecturer prior to seeking departmental approval.
PS2234 - Introduction to Comparative Politics
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): PS2204B
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module introduces to students some major approaches to comparative politics, including system perspective, case study, comparative approach, rational choice, and cultural approach. Specific cases are used to illustrate how people have applied these approaches in research. It also covers selected topics in comparative politics, such as democratisation and democratic consolidation, revolution, and ethnic conflicts. Much of the discussion will be based on specific cases. This introductory module is offered to students who want to gain basic knowledge of comparative politics.
PS2236/EU2217 - European Politics
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): EU2208, EU2217, PS2213, PS2206B
Cross-listing(s): EU2217
This introductory course gives students a basic understanding of the ideas, institutions, and actors that influence the political life of modern Europe. We explore the domestic politics of several European states including France, and the U.K., as well as relations among European states before and after World War II, with special attention to European integration. While most of our attention will be devoted to Western Europe, we will discuss political transitions in Eastern Europe and the process of EU expansion. The module is intended for students in European Studies, Political Science, and others with an interest in Europe.
PS2245 - Southeast Asian Politics
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): PS2215B, SE2213
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module will serve an introduction to the nature and dynamics of government and politics in Southeast Asia, especially state-society relations. Hence, the module will look at government and politics in countries like Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Thailand, Vietnam, and Burma. This module is aimed at students across all faculties and at all levels interested in learning about political dynamics in Southeast Asia. Its primary objective is to expose students to the region, and provide a basic foundation in government and politics of Southeast Asia from which students can further acquire/develop specialised knowledge.
PS2247 - South Asian Politics
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): PS2214B, PS2217B, PS3217B, SN2211, SN3221
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module is divided into two parts. The first half of the module has a comparative politics focus. It will examine the contemporary politics of South Asian states, focusing on their political culture, institutions and processes and political change and development. It will also treat issues like ethnicity, religion, regime legitimacy and the relationship between violence and democracy. By studying these issues comparatively we can discern regular patterns in the behaviour of individuals and groups and understand how their demands are processed and met. The second part of the module will adopt a thematic approach to explain the various factors that have shaped intra-regional relations. This will include the role of external powers and also the spill over effect of domestic conflicts. Foreign policy objectives of the regional states and their threat perceptions will be the principal area of focus. The module will also deal with issues of regional order and stability. The target students are those enrolled in South Asian Studies Programme and Political Science.
PS2248 - Chinese Politics
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): PS3205B, PS3250
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This course is an introduction to contemporary Chinese politics. After a survey on China’s political culture and tradition, the rise of modern China and Chinese Communism, it discusses a range of nation-building issues in the People’s Republic of China. These include the role of ideology, developmental strategies, political institutions, and state-society relations. Having examined the domestic political issues, the course proceeds to analyse Chinese foreign policy. Topics to be dealt with include China’s relations with the U.S., Japan, Russia, European Union, and ASEAN. The problems related to the reunification of mainland China and Taiwan are also covered.
PS2249/GEK2003/SSA2209 - Government and Politics of Singapore
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): GEK2003, GEM2003K, PS1102, PS2101, PS2101B, SS2209PS, SSA2209
Cross-listing(s): GEK2003, SSA2209
This course examines a number of areas in Singapore’s domestic politics with the following objectives: identify the key determinants of Singapore’s politics; understand the key structural-functional aspects of Singapore’s domestic politics; examine the extent to which nation building has taken place in Singapore; and analyse the key challenges facing Singapore and its future as far as domestic politics is concerned. The course examines both the structural-functional aspects of domestic politics as well as issues related to nation building, state-society relations and the likely nature of future developments and challenges.
PS2254 - American Government and Politics
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
The American system has been a model for countries around the world and, more recently, a lesson in the dangers of partisan politics. This module provides an overview of political institutions and practice in the United States. It examines the Constitution, the Presidency, Congress, and Judiciary, the federal system, the party system, and presidential and congressional elections. Because it has been intensively studied, the American political system provides a good introduction to the study of political science.
PS2255/GEK2025 - Politics of the Middle East
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): GEK2025
Cross-listing(s): GEK2025
This module provides a comparative overview of politics in the Middle East, giving particular attention to the history, societies, and cultures of the region. It considers some of the forces shaping its politics and discusses, selectively, major issues and challenges facing states in the Middle East today.
PS2257 - Contemporary African Politics
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
Drawing on the rich social science literature on the government and politics of contemporary Africa, the course will address a set of critical questions that will have important implications for the well-being of the people of the continent and the world in the twenty-first century. What have been the sources of the political and economic crisis that gripped Africa? What has been the net impact of the international interventions in the continent that in response to these crises? What explains the revival of democracy and economic growth in some parts of the continent? Will it last?
PS3225 - Political Islam
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module explores the rise, transformation, and sources of appeal of Islamist movements and organizations around the world. It is divided in two parts: the first part reviews the development of Islamic political thought from late nineteenth century to the present, covering the work of modernist, neo-revivalist and liberal Islamic thinkers. The second part examines Islamist ideas in practice in order to flesh out the ways in which Muslim ideologues have inspired forms of political mobilization and contestation. Primarily focusing on the Middle East, the second part investigates specific Islamist movements in historical and comparative perspective.
PS3236 - Ethnicity and Religion in Asian Politics
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): PS3201, PS3206B
Cross-listing(s): Nil
One of the main features of Asian politics and government is the complex nexus of ethnicity, religion, and the state. This module focuses on the colonial formation and postcolonial continuation of these ethno-religious features of politics, known as the politics of identity in Asia. It explains some major ethnic and religious conflicts in Asia; their impacts on national politics, party systems, state structures, and government policies; and the role of the state in this regard. The module is available to all year 1-3 students at NUS.
PS3237 - Women and Politics
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): PS3207B
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module examines established political theories and ideologies in addressing gender equality and representation in politics. It also presents various traditions in feminist political thinking and evaluates their intellectual contributions to politics. The second part of the module examines the practical dimensions of gender politics such as women’s movements and national and international conventions and institutions. It analyses the relationship among gender, class, and ethnicity, and examines the cultural and religious perceptions of these identities. The module is available to all year 1-3 students at NUS.
PS3263 - Comparative Study of Development
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): PS2205B, PS2235
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module examines the politics of economic development and underdevelopment. Students are introduced to major political issues in developing countries and to political science frameworks for understanding those issues. Themes covered include state-building, the relationship between development and democracy, the state’s role in industrialisation, development problems and development policy. Specific countries are used as cases to illustrate - and criticise - arguments about politics and development, but the focus in this module is on common themes rather than the political histories of particular nations.
PS3265 - Civil-Military Relations
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): PS1101E
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module surveys major themes and debates in the study of civil-military relations. The study of civil-military relations addresses a simple puzzle: can we have a military strong enough to protect civilians yet not so strong as to ignore or subvert civilian authority? A military strong enough to defend the state from external enemies is also strong enough to seize power. How can a state have a strong military capability without being dominated by it? How do political leaders and military organizations interact with each other and with the larger society, and how do their cultures overlap and diverge.
PS3273 - Singapore Politics in Comparative Perspective
Units: 4
Prerequisites(s): NIL
Preclusion(s): NIL
The module connects Singapore politics to important themes in the study of comparative politics. It examines the relevance of political science concepts for understanding local politics, and investigates how the study of Singapore might inform debates in comparative politics. The issues to be considered may include: state-building, democratisation, party politics, racial politics, civil rights, judicial politics, identity and citizenship, and the state’s role in industrialisation.
PS3274 - Environmental Politics
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module introduces students to competing concepts and arguments in environmental politics. The module will enhance students' understanding of the ways in which political and economic institutions, regimes, culture, and norms interact with environmental outcomes at local, regional, and global levels. Students will also learn the roles different actors and institutions play in global environmental governance.
PS3275 - Regimes in Transition
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): PS1101E
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
Few things are more dramatic than the collapse of a political system, whether through violent conflict or peaceful negotiations. Explaining why regimes break down and why new ones emerge are among the most important questions in political science. This module looks at the conditions under which regimes unravel, focusing on the breakdown of democratic institutions, the rise of populism, and conversely, transitions away from various types of authoritarian regime, using case studies from Southeast Asia. PS2234, while not a pre-requisite, is strongly recommended.
PS3276 - Comparative Political Behaviour
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): NIL
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This upper-level seminar surveys the literature on comparative political behaviour with cases drawn from South, Southeast, and East Asia. Given how broad the comparative political behaviour literature is, we will cover only some of the most studied topics. These topics include voting behaviour, political identities, and political participation. Since no individuals live in a vacuum, we also will cover how individuals and political behaviour are constrained by political system and political culture.
PS4202 - Political Parties and Elections
Units: 5
Prerequisite(s):
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS with a minimum GPA of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module covers political parties and electoral systems in both established and new democracies. In the West, political party systems reflect highly institutionalised electoral systems and are relatively stable. In much of the world, however, political parties are less institutionalised and more responsive to volatile electorates than those in the West, and many new democracies have failed to develop even minimally stable party systems. The aim of the module is to provide students with a good grasp of the issues and current research on political parties and elections in the West, in Asia, and around the world.
PS4205 - Contemporary Politics of Southeast Asia
Units: 5
Prerequisite(s):
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS or 28 Units in SE with a minimum GPA of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS, 28 Units in SE or 28 Units in GL/GL recognised non-language modules, with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module aims to highlight contemporary issues besetting countries in this part of the world with the goal of helping students to better understand the myriad problems and challenges confronting Southeast Asian states, as well as assess their relative effectiveness in dealing with these challenges. This module will discuss the politics of key nation building issues such as ethnicity, religion, and class and examine how the governments manage other pressing challenges such as the forging of national identity, globalisation and new security threats. This module is targeted at students in the advanced years, specifically the Honours Year.
PS4221 - Contemporary Politics of Northeast Asia
Units: 5
Prerequisite(s):
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS with a minimum GPA of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS, or 28 Units in SC, 28 Units in GL/GL recognised non-language modules, with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module seeks to explain similarities and differences between the countries of Northeast Asia and to broaden and sharpen students’ understanding of the various political, economic and social issues confronting this region. Focusing on China, Japan and Korea, the module will consider the principles and practices of democracy and the obstacles to democratic transition. It will also consider a selection of overlapping topics and issues such as political parties and elections, corruption, nationalism, civil-military relations, civil society, local politics, women and politics, economic reform, leadership and the media.
PS4224 - State and Society
Units: 5
Prerequisite(s):
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS with a minimum GPA of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS or 28 Units in GL/GL recognised non-language modules with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): PS4204
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module introduces students to some of the major themes of comparative political sociology through the lens of a clearly established literature that draws from a variety of national and sub-national case studies. It focuses on the relationship between civil society and the state and on the institutions and processes that mediate that relationship. Topics covered include contemporary theories of the modern state; political culture and civil society; revolutionary and non-revolutionary political regime change; clientelism; and corporatist and non-corporatist forms of interest group intermediation.
PS4228 - Comparative Democratic Politics
Units: 5
Prerequisite(s):
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS with a minimum GPA of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS, or 28 Units in SC, with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
Democratic politics are an integral part of Comparative Politics. This module addresses major issues of democratic politics since World War II. The module has three parts: contemporary democratic theory, patterns of democratic transition since the 1980s, and democratic consolidation. The module combines historical, theoretical, and comparative approaches to help students understand the democracy as a political system, the merits and demerits of democracy, and the driving forces behind democratization in the contemporary world.
PS4234 - Identity Politics
Units: 5
Pre-requisite: (a) Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS or 28 Units in GL/GL recognised non-language modules, with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This is a course that explores the origins, reproduction, and effects of social identity from a variety of perspectives. The sources of identity that are investigated include the self, group, society, and state, as well as their more complicated combinations. The identities whose origins, maintenance, and effects we study are nation, ethnicity, gender, religion, sexuality, and race. The approaches we take to make sense of identity politics include writings in political science, social psychology, sociology, history, anthropology, and cultural and post-colonial studies.
PS4312 - Seminar in European Politics
Units: 5
Pre-requisite: Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS or 28 Units in GL/GL recognised non-language modules, with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module introduces significant questions of politics in Europe. It teaches students to analyse the ideas, institutions, actors, and interests that influence European politics. We explore the domestic politics of European states including Germany, France, and the U.K., and relations among European states after World War II, with particular attention to European integration. While most of our focus will be devoted to Western Europe, we will discuss political transitions in Eastern Europe and the process of EU expansion. We will critically assess debates in European politics on issues like migration and refugees, Brexit, the European economy, foreign and security policy.
PS4313 - Seminar in Comparative Political Economy
Units: 5
Pre-requisite: Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS or 28 Units in GL/GL recognised non-language modules, with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module introduces theories of political economy in a comparative perspective – from classical liberalism to critical approaches. It covers institutional, interest- based and ideational analysis. It examines key topics in political economy including the causes of economic growth; state-market relations; markets for goods and services, finance and labour; macroeconomic management; debt, inequality, and redistribution; economic reform in industrial and developing states. This module is designed to help students critically assess the classic and current research literature on how states and markets are organised, justified, and transformed over time and across nations – with a particular focus on the varieties of capitalism.
PS4881 - Topics in Comparative Politics
Units: 5
Prerequisite(s):
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS with a minimum GPA of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module will offer special topics in comparative politics. Students should check the topics that are on offer in a given semester before enrolling in the appropriate section of the module.
PS4881B - Malaysian Politics
Units: 5
Prerequisite(s):
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS with a minimum GPA of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS, or 28 Units in SC, or 28 Units in GL/GL recognized non-language modules, with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module examines major issues in Malaysia’s political landscape today and in recent times. It considers tensions and controversies over ethnicity, religion, party politics, money politics, governance, democracy and civil society, national identity and national integration, and globalization.
PS4881C - Labour Politics
Units: 5
Prerequisite(s):
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS with a minimum GPA of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS, or 28 Units in SC, or 28 Units in GL/GL recognized non-language modules, with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This seminar considers working class participation in the political economy, including labour market regulation, national labour administration, state-labour ties, labour-business relations, the structural conditions underpinning labour-capital relations and labour representation in the political arena. Attention is given to corporatist, neo-corporatist and pluralist forms of labour politics and to some of the ways labour enters the political system: for example, as autonomous, state or party-dependent, non-dependent party-affiliated, pressure group, social movement or unorganized activity. Issues of format, scope, and participation in collective bargaining will be addressed, as will principal-agent and other collective action logics.
PS4881D - Money and Politics
Units: 5
Prerequisite(s):
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS with a minimum GPA of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This seminar examines the relationship between private wealth and political power. Most polities claim to pursue public ends, yet many leaders have close links to private money. In democracies, elections are supposed to produce accountable officials, yet campaigns depend on funding from corporations and individuals. This module addresses questions about the ‘dirty’ side of politics: Why does vote-buying occur in some situations but not others? What is the role of organised crime in the business-politics nexus? How representative are elected leaders if they are also indebted to campaign financiers? These themes have wide relevance and we will study them in a variety of contexts, from local struggles in the developing world to American presidential elections.
PS4881G - Topics in CP: POLITICS OF THE KOREAN PENINSULA
Units: 5
Prerequisite(s):
Cohort 2019 and before: Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS or 28 Units in GL/GL recognised non-language modules, with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2020 onwards: Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS, with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module offers an introduction to key issues in Korean politics. We cover the politics of both regimes on the Korean Peninsula, as well as inter-Korean relations. Although the module focuses on the domestic politics of Korea, the peninsula's politics cannot be understood without reference to the broader regional and international context. The module therefore bridges comparative politics and international relations.
PS4881H - Topics in CP: Chinese Politics
Units: 5
Prerequisite(s):
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS, with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track, and PS2248 Chinese Politics.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module addersses some of the major issues of contemporary Chinese politics. The issues to be discussed include the politics of economic privatisation, social stratification and emerging class conflicts, rural reforms, poltical corruption, new forms of representation and participation, social-political pluralism, central-local relations, Taiwanese democracy, and the prospects of China's politicial transition. To help the student better understand the dynamics, consequences, and implications of China's polticial, economic, and social developments since 1978, this module combines theoretical and comparative approaches that extend its scope beyond an empirical study of China.
PS5312R - Seminar in Comparative Politics
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): PS5213, PS6301B
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This seminar will survey the methodology, dominant approaches and theories in comparative politics. The seminar will place emphasis on methodological and theoretical issues that are common to the study of comparative politics. Classic works by leading comparativists will be used to illustrate the strengths and weaknesses of the existing methodological and theoretical approaches to the study of comparative politics.
PS5313R - Seminar on State and Society
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
Every state tries to govern effectively and to win popular compliance with its rule. Why are some states more successful than others in achieving this paramount objective? This seminar explores some answers to this question through intensive reading and discussion of some major works in comparative politics.
PS5319R - The American Presidency
Units: 4
Pre-requisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module surveys the foundations of American presidential authority and power, traces the historical development of the institution, and evaluates various scholarly approaches to understanding the American presidency. The American presidency was the first of its kid, the distinguishing feature of one of two prototypical systems of government that has come to be known as presidentialism, in contrast to parliamentarism.
PS5321R - Seminar in Chinese Politics
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): PS6316
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This seminar addresses some major questions of politics in China in recent decades. These include leadership succession, economic privatization, new forms of social stratification, representation and elections, civil society, changing rural governance, corruption, protest politics, the role of the Internet, and ethnic politics. The module will review current scholarship and provide a foundation for masters and doctoral students planning to undertake research on Chinese politics.
PS6314 - Advanced Studies in Asian Politics
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module is meant to familiarise students with some of the more important domestic political issues in Northeast and Southeast Asia. It will examine a number of common themes that are relevant to both regions like political development and stability, state-society and civil-military relations and comparative democratisation. The module is ideal for students who would like to acquire a broader and deeper understanding of Asia and reflect on sub-regional differences.
GE2222 - Politics and Space
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module introduces students to the major thematic concerns that have traditionally shaped political geography as a sub-discipline. It also allows students to engage with emerging issues that are likely to become focal points in shaping future debates among political geographers. The aim of the module is to explore the co-constitutive relationship between politics and space. As the political organization of society has spatial consequences, so too does geography influence our understanding of political relationships. These relations are negotiated and contested in multiple ways that cut across different locations, scales, and temporalities. Accordingly, we will examine political concerns, disputes, accommodations, and consequences from a geographical perspective, where students can expect to acquire a critical appreciation for the historical trajectories and evolving implications of states, sovereignty, territoriality, nationalism, colonialism, democracy, ethnic conflict, policing and crime, terrorism, war, environmental justice, and political activism.
GL4886A - Citizenship and the Politics of Belonging
Units: 5
Pre-requisite: Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in GL or GL recognised non-language modules or 28 Units in PS with a minimum GPA of 3.2 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module critically examines the various contested definitions, practices, policies and law of citizenship found around the world. It explores how historical legacies, levels of economic development, regime transformation, political geographies, technological changes, and social forces shape who belongs (an who does not) to a particular political community or nation-state. The module systematically applies key concepts to case studies from around the world to highlight how and why actors bestow, deny, and contest citizenship as well as the policy and normative implications that flow from these processes.
GL4887A - The Modern Middle East in the Age of Globalisations
Units: 5
Pre-requisite: Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in GL or GL recognised non-language modules or 28 Units in PS with a minimum GPA of 3.2 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This course examines the impacts of globalizations on the modern Middle East from 1798 to the present. During this period of local, regional, and global transformations, the Middle East witnessed the collapse of the Ottoman and Qajar Empires, World War One, World War Two, colonialism, decolonization and the Third World Movement, the nation-state building projects of the newly created Arab countries, the Cold War, the global oil politics, and most recently the Arab Spring. The course may focus on connections between the Middle East and other regions including Asia in the context of those global events.
GL4888A - Justice and Emerging Technology
Units: 5
Pre-requisite: Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in GL/GL recognized non-language modules, or 28 Units in SC or 28 Units in PS, with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module examines moral and public policy challenges presented by emergent technologies that challenge notions embodied in current institutions and theories of what is natural and what is subject to human manipulation, and even create entirely new domains of human activity and interest. These new technologies operate globally and often rapidly, generating consequences far beyond the location of their users. The module studies how social and political institutions? New or old? Structure, regulate, develop, and distribute these technologies in accordance with various conceptions of justice.
JS2223 - Government and Politics of Japan
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module is designed to help students understand fundamental issues and problems of contemporary Japanese politics and policy-making. Major topics include the formation and collapse of the one-party dominant system, electoral reforms, party and factional competition with a focus on the Liberal Democratic Party, coalition politics, roles of the Prime Minister, systems in the Cabinet and the Diet, central bureaucracy, and features of the policy-making system. It will also review the implications of domestic politics for Japan's foreign economic policy. Readings can be utilized as basic backgrounds for the topics, while the lectures will focus on the current political issues and reforms.
JS4227 - Japanese Political Economy
Units: 5
Prerequisite(s):
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in JS with a minimum GPA of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in JS or 28 Units in PS, or 28 Units in GL/GL recognised non-language modules, with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module is designed to promote students' understanding of some of the salient features of Japan's political economy, especially the roles of politicians and bureaucrats in the conduct of industrial and foreign economic policy. The module will review major research on Japan's political economy written from historical, theoretical and comparative perspectives. By exploring the changing international images of Japan in the field of political economy, the module aims to highlight: the role of the government in Japan's high post-war economic growth and features of its industrial policy-making processes; the relevance of high growth in other East Asian economies in comparison to the Japanese case; the different schools of thought on Japan's economic policy and the evolution of US-Japan trade friction in the 1980s; and Japan's approaches to and initiatives in deregulation in the 1990s.
JS4233/ JS4233HM - Japan’s Immigration Politics in Global Perspective (Comparative Politics subfield)
Cohort 2020 and before:
Units: 4 (JS4233)
Prerequisites: Completed 80 units, including 28 units in JS or LAJ, with a minimum of 12 units in JS or 28 units in GL/GL recognized nonlanguage courses.
Cohort 2021 onwards:
Units: 5 (JS4233HM)
Prerequisites: Completed 80 units, including 28 units in JS or 28 units in GL/GL recognised non-language courses, with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
International migration is currently one of the most difficult challenges facing policymakers in advanced democracies. This seminar will explore how this global challenge has been addressed in Japan – a “new” country of immigration. Through comparative lenses, we will review the state-of-the-art theoretical and empirical literature that explores the following themes: the question of borders, policy actors, economic and forced migration, migration and security, the ethics of immigration control, citizenship, diaspora politics, and immigrant integration and multiculturalism, among others.
NM5201R - State and Civil Society in the Information Age
Units: 5
Pre-requisite: (a) For CNM major who has accumulated 120 Units (b) For CNM, FASS, and SoC graduate students.
Preclusion(s): IF4880A, IF5201
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module will expose students to advanced topics in state-society relationship and governance within the context of rapid changes in information and communication technologies (ICTs). It addresses how the notions of `community', 'citizenship', and 'democracy' have been changed by the creation of a transnational public sphere due to ICTs. The module will also address how the emergence of an informational economy changes the role of the state, especially in terms of preparing society for the challenges ahead. Works of John Urry, Manuel Castells, Bob Jessop, Frank Webster and David Lyon, among others, will be discussed and critiqued.
SE4227 - Nationalism in Southeast Asia
Units: 5
Prerequisite(s):
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in SE or 28 Units in PS, with a minimum GPA of 3.50 or be on Honours track.
Cohort 2012 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in SE or 28 Units in PS or 28 Units in GL/GL recognised non-language modules, with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
The module provides a critical study of various theories and practices of nationalism in Southeast Asia from an interdisciplinary perspective. What is the relationship between colonialism and the development of national attachments and nationalist politics? What roles have ethnicity and religion played in the emergence of national and state identities in Southeast Asia? Students will address these questions and examine the rise of nationalism as a leading political principle and the fate of the nation-state in an increasingly globalized and globalizing world.
SE5294R - The Politics Of Environment in SE Asia
Units: 5
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
The growth and development that has taken place not only in the Southeast Asian region but also in the rest of the world is commonly viewed to have a negative impact on the environment in the region. Is it necessarily true? Are there positive effects as well? This module will evaluate the link between the developmental process and the environment including an analysis of the problems, the proposed solutions, and the actual policies implemented. The module provides not only a Southeast Asian perspective on the environmental and the developmental issues facing the region, but also a geographical outlook. This emphasises the sharing of natural areas and resources among nation-states and their peoples in Southeast Asia given the historical background of the region with its impact on national borders and the composition of both the population and society. The outcome on nature and society relations seen in Southeast Asia reflect conditions specific to the region and its geography. This module is aimed at understanding both these specific conditions and the wider as well as external factors that have an impact on environment in Southeast Asia.
SC3205 Sociology of Power: Who Gets to Rule?
Units:: 4
Prequisites: Nil
This course introduces students to political sociology which is broadly concerned with understanding such phenomena as power, state and society relations, and the nature and consequences of social conflict. The main concerns of this course are issues pertaining to modern society and capitalist development, referring to diverse cases from Western Europe to Southeast Asia. We will also be looking at the state, civil society and societal movements, including that of labour, and such contentious contemporary issues as economic globalization, US global hegemony, and terrorism.
SC4201 - Contemporary Social Theory
Units: 5
Prerequisite(s):
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in SC with a minimum GPA of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in SC, or 28 Units in PS, with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module maps out the main currents of contemporary social theories ranging from the legacy of the classical tradition, comparative-historical sociology, interpretative sociology, functionalism and neo-functionalism, rational choice, globalization theories and the macro-micro debates. In exploring the nature and status of social scientific theories we deal with the universalism/ relativism debate and link it to the problems of globalized vs. indigenized social theories. This module is mounted for students with a keen interest in social theories.
SC4217 - Social Movements and Collective Behaviour
Units: 5
Prerequisite(s):
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in SC with a minimum GPA of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in SC, or 28 Units in PS, or 28 Units in GL/GL recognised non-language modules with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
The course focuses on developing a framework for constructing and rethinking factors (be they economic, political, cultural) that have led to the emergence, development, and maintenance of certain forms of collective behaviour. It will also examine these theories through various case studies of social movements such as historical revolutions, and the "new" social movements of Europe. Topics covered include the rationality of collective action; history of social movement theory; the role of individuals, social groups and institutions in social movements; and their impacts. This module is mounted for students with interest in social movements.
SC4218 - Religions, Secularity, Post-Secularity
Units: 5
Prerequisite(s):
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in SC with a minimum GPA of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in SC, or 28 Units in PS, or 28 Units in GL/GL recognised non-language modules with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module is designed to develop a nuanced understanding of forms of religiosity in the present. One aim of the module is to explore connections between the realms of religion and politics, particularly within the framework of secular states. The module examines the notions of `secularity? and `post-secularity? and queries their relevance for the contemporary moment, within a comparative, historical perspective. Is it useful to invoke the concept of `secularism? to make sense of encounters between religious and political domains? Do the ideas of the `separation of church and state? and `state non-interference in religion? help in these efforts?
SC4882A - Perspectives on State and Society
Units: 5
Prerequisite(s):
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in SC or 28 Units in PS with a minimum GPA of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in SC or 28 Units in PS or 28 Units in GL/GL recognised non-language modules with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): SC4215A Perspectives on State and Society
Cross-listing(s): Nil
What is the impact of globalization on the state, and how can we come to terms with these two concepts? What is the future form of state-society relations, and do concepts such as democracy, civil society, national identity and rethinking as we move into a highly connected world? Using cases from around the globe, students will be exposed to the very broad perspective offered by comparative and historical analysis. The course will initiate thinking about social welfare options and citizenship in a globalized world. Through historical and comparative analyses, critical questions about the role of the state in welfare provisions, economic development, and democratic development will be examined. This module is mounted for students throughout NUS with interest in the state-society relationship.
SN2213 - South Asian Democracies - Violence, Conflict, and Hope
Units: 4
Pre-requisite: Nil
Preclusion(s): PS2247 South Asia: Politics and Foreign Policy
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module is about the politics of democratization in South Asia, a region with a long history of interstate and intra-state conflict. The post-colonial separation of India into India, Pakistan, and Bangladesh has caused cross border tensions and paved the way for military intervention in the domestic politics of Pakistan and Bangladesh. The diverse interests of ethnic and religious communities are testing the legitimacy of majoritarian democracy and the limits of claims for autonomous government. This module examines the institutional structures, State-citizen relations, and identity politics in South Asia’s democratic experiments to find hope for democracy in a polarized world.
PS2237 - Introduction to International Relations
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): PS2207, PS2207B
Cross-listing(s): Nil
Designed as an introductory theoretical module, it covers the basic concepts of International Relations in two halves. The first introduces the concepts of nation, state, sovereignty, non-state actors and their implications for the coexistence of nation-states, as well as a brief roundup of the instruments of conducting relations among them. The other offers a grounding in the major schools of thought on International Relations, namely realism, liberalism/pluralism and revolutionism. Additionally, there will be topics on radical perspectives such as feminism, constructivism and postmodernism. It is hoped the module will provide students with a foundation for other courses in the sub-field.
PS2238 - International Politics of Northeast Asia
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): PS2208B
Cross-listing(s): Nil
The aim of this module is to understand the international relations of Northeast Asia. The first part of the module provides a historical and theoretical overview of the subject. The second part assesses competing explanations for the international behaviour and interactions of the region’s major powers. The final part examines selected multilateral/ transnational issues as sources of potential conflict and cooperation.
PS2239/GEK2010 - Foreign Policy and Diplomacy
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): GEK2010, GEM2010K, PS2209, PS2209B
Cross-listing(s): GEK2010
This exciting field of study provides an understanding of the foreign policy processes and behaviour of actors in world politics. These actors are largely but not exclusively, the nation states. The module deals with various concepts, frameworks and approaches to the study of foreign policy and diplomacy. It explains both the external and internal determinants shaping foreign policies of different states. It also focuses on foreign policy implementation by analysing the role of diplomacy, economic statecraft and the use of military force. The module is meant for students who want to understand how states conduct their external relations.
PS2250 - International Politics of Southeast Asia
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): PS3215, PS3241, GEM3003K, PS3211B
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module examines the evolution of Southeast Asia as a region in international politics. The emphasis of the module is on the impact of external actors on Southeast Asia, albeit the module will also deal with regional developments and indigenous initiatives. Initially, the module will deal with past developments that affected the region. The second half will deal with more contemporary regional developments, some of which are still ongoing. This module will be extremely useful for students who would like to understand regional political issues.
PS2251 - The Region in the Postcolonial World
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
In this module, students will study postcolonial regions in Asia, Africa, the Middle East, and Latin America. They will discuss questions such as: What makes a region? Who makes a region? How has the experience of colonialism shaped the region? What are the models of regional cooperation and integration, and whose models are they? How do regions ‘interact’ with postcolonial global structures and dynamics? Students are encouraged to compare different regional experiences, and draw from this breadth of knowledge to critically evaluate the concepts and theories they will learn.
PS3216 - Global Health Governance and Politics
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): PS2237
Preclusion(s): YSS3324
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This course is designed for students interested in the intersection of international relations and global health. It will introduce students to various issues and topics in global health. Questions explored in this course include: What are the health threats and opportunities that arise with globalization? Who are the main actors and what are the major institutions influencing processes of global health governance? How do existing institutional arrangements function in responding to global health challenges? To engage comprehensive examination of these key issues, we will turn to International Relations concepts, such as power, legitimacy, soft vs hard law, regime, and normative change.
PS3238 - International Political Economy
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): GEK3001, GEM3001K, PS3207, PS3208B
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This course presents a broad overview of international political economy (IPE). It introduces the student to main theoretical approaches, concepts and substantive issues in the IPE field, and help him/her better understand the relationship between power and wealth and the interplay of economics and politics in the world arena. After a critical evaluation of major theoretical perspectives on IPE, this course examines the politics in some core issue areas, such as economic interdependence, international division of labour, international trade, multinational corporations, regional cooperation, and North-South relations.
PS3239 - International Conflict Analysis
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): PS3209B
Cross-listing(s): Nil
The module aims to provide a broad understanding of international conflict situations, conflict behaviour and attitudes. It deals with the nature, type and sources of conflict. Based on insights from general conflict studies it explains conflict pathologies and the debilitating effects of protracted social conflicts. It also analyses various conflict resolution strategies by focusing on negotiation techniques, third party mediation and intervention. Bearing in mind that conflicts are mostly transformed rather than eliminated the module assesses the experience of peace-promotion and peace-building in post-conflict societies. The module is meant for students keen on a multidisciplinary approach to international conflict.
PS3240 - International Security
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): PS3210B
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module examines key issues pertaining to international security including: the various approaches to studying international security, the nature of interaction among various levels (national, regional, international) of security, and the major security threats caused by the expansion of conventional arms, proliferation of nuclear arsenal and the spread of biological and chemical weapons. The rise of non-traditional security threats in world politics, especially Southeast Asia, and of Asia, particularly China, as a security concern internationally is also analysed.
PS3242 - US Foreign Policy
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module considers the foreign relations of the United States. It covers both the institutions and practices that shape the making of US foreign policy and the substantive policies that emerge from the policy process.
PS3247 - The Rise of China and International Order
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This course explores a number of theoretical approaches in international relations to understand the rise of China as an example of the general phenomenon of hegemonic transition. In previous cases of hegemonic transition, there has been great power war. The various theoretical approaches covered will include: power transition theory, hegemonic stability theory, liberal interdependence, world-systems theory, democratic peace, neoliberal institutionalism, neorealism, balance of threat, neo-Gramscianism, and constructivism.
PS3249/SSA3205 - Singapore's Foreign Policy
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): PS3219B, SSA3205, SS3205PS
Cross-listing(s): SSA3205
This module analyses Singapore’s outlook towards the world with particular reference to countries in the West and Asia. It examines the following key issues affecting Singapore’s foreign policy: problems of a small state, factors influencing the worldview, the key foreign policy principles and precepts, the operationalisation of relations towards different countries; and the key differences in outlook towards the world in the Cold War and post-Cold War periods. The course is mounted for students throughout NUS with interest in Singapore and particularly its foreign policy.
PS3251 - International Organisations
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): PS1101E
Preclusion(s): PS3254, EU3228
Cross-listing(s): Nil
In this module, students will study the international organisations that constitute a crucial part of the global institutional architecture. Based on an understanding of the literature on international relations and organisations, the module will seek to address a set of critical questions: Why are international organisations created? What are their objectives, and how are these objectives achieved? What effects do international organisations have on the practices of international relations? Through the consideration of these questions, students will gain empirical and theoretical insights into global governance and international relations indispensable to any student of Political Science and International Relations.
PS3252/GEK3006 - Human Rights in International Politics
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): GEK3006
Cross-listing(s): GEK3006
This is a module that examines theories of human rights since 1945, and the practice of promoting or rejecting these ideas as universal “goods” in international relations. Students will critically examine NGO issue advocacy, western states’ “ethical” foreign policies; and the “Asian values” counter-challenge. This module relates the subject of human rights to political philosophy, international law, the UN system, morality, national interest, and values/ideology in foreign policy.
PS3272 - The International Relations of Sub-Saharan Africa
Units: 4
Prerequisites(s): NIL
Preclusion(s): NIL
The module examines the insertion of Sub-Saharan Africa into the world, and looks at both intra-African international relations, as well as how African states have interacted with various external actors. Students will examine the implications of issues such as governance, security, and development aid for Africa’s international relations. They will also learn about the international relations of key African states with countries outside Africa.
PS3311 - International Ethics
Units: 4
Prerequisites(s): NIL
Preclusion(s): (Yale-NUS Module) YSS3270 Ethics and Global Affairs and PS3233 Political and International Ethics
This module explores the ethical dimension of international relations. It takes as its point of departure the conviction that international relations, like all realms of human conduct, is intelligible in questions of obligation, right, good, and so forth. The module interrogates prominent ethical languages of international relations, including moral scepticism, sovereignty, war, international law, and human rights. It then considers how these languages arise and conflict in a range of contemporary international issues. Particular emphasis is placed on excavating the ground on which ethical choices are made, defended, and judged.
PS3312 - World Orders
Units: 4
Prerequisites(s): NIL
Preclusion(s): NIL
Cross-listing(s): NIL
Ideas and concepts derived from European experience—anarchy, sovereignty, balance of power, and so forth—dominate thinking about world order. This module challenges this dominance by problematising European narratives and by examining extra-European approaches. Particular attention will be given to thematic issues, such as empire and race, as well as Asian, Islamic, and Pan-African understandings of world order. Consideration will also be given to the adequacy of European ideas and concepts, and to alternative vocabularies of world order. The module is historical and philosophical in orientation, with theoretical questions being at the centre of inquiry.
PS3880D - Politics of the United Nations
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module examines the political dynamics entailed in and produced by the United Nations System. Using both traditional academic analysis and experiential learning (an in-class simulation) the module probes three of the most politicized aspects of the UN: its institutional design; its mandate to pursue collective international security; and the UN’s efforts to globally advance human development.
PS3880E - Human Trafficking in Southeast Asia
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module explores the politics of human trafficking in Southeast Asia. It critically examines questions such as the following: What are the causes and consequences of human trafficking in the region? What are the different forms of trafficking (e.g., sex trafficking, forced labour, child soldiers)? How does trafficking involve human rights and to what extent are these rights enforced? How do governments, the media, and others portray trafficked persons – and more importantly, how do they portray themselves? The module also provides students with educational exercises in the field, applying relevant theories and research methods.
PS3880F - Quantitative Approaches to International Relations
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Students must have read PS2237 Introduction to IR and PS3257 Political Inquiry
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module introduces students to quantitative approaches to the scientific study of international political and economic relations. It focuses on current quantitative research on such diverse topics as conflict and peace, international trade, investment, and monetary relations, and the design and effectiveness of international institutions in protecting human rights and the environment. In addition to studying and evaluating the contemporary academic literature, this modules requires students to actively contribute to and improve on existing international relations research using advanced quantitative methods. The module provides students with the necessary statistical tools and skills to do so.
PS3880H - The Politics of European Integration
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module considers European integration as an advanced experiment in supranational governance. It examines the main theories of European and regional integration, including neofunctionalism, liberal intergovernmentalism, and Europeanization theory, and applies these theories to understand debates about the EU’s identity, its imagined ‘end point’, arrangements for sharing power between member states and central institutions, and possible futures.
PS4203 - China's Foreign Policy
Units: 5
Prerequisite(s):
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS with a minimum GPA of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS or 28 Units in GL/GL recognised non-language modules, with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module examines some major issues of contemporary Chinese politics, political economy, and policy processes as they affect Chinas relations with the rest of the world. It covers both the institutions and practices that shape the making of Chinese foreign policy and the substantive policies that emerge from the policy process.
PS4206 - Regional Security in the Asia Pacific
Units: 5
Prerequisite(s):
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS with a minimum GPA of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS or 28 Units in GL/GL recognised non-language modules, with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
The module introduces the trends, approaches, and limitations of security studies in the Asia-Pacific. It explores major institutional arrangements of regional security and linkages between these regional arrangements and international security structures. It also analyses contemporary changes in the issues and priorities of security and the newly emerging security concerns in the Asia-Pacific. The implications of domestic political changes for regional security are also considered. The module can be read by honours and postgraduate students in Political Science.
PS4208 - Theories of International Relations
Units: 5
Prerequisite(s):
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS or 28 MCS in SC with a minimum GPA of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012 onwards:
Cohort 2012 onwards: Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS or 28 MCS in SC with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module explores major theoretical debates in international relations (IR). After discussing some of the standards by which we might evaluate theories, we will examine some realist, liberal, and 'alternative' theories of international relations, and the classic debates between these perspectives. Theories are applied to major aspects of international relations such as trade, war, alliances, and stability, for individual states, for particular groups of states, and in the international system as a whole. We will also explore the role of domestic politics in foreign policy. The module is designed for Political Science Honours students.
PS4216 - The Study of War
Units: 5
Prerequisite(s):
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS with a minimum GPA of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS or 28 Units in GL/GL recognised non-language modules, with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
Traditionally, as a discipline, International Relations have treated war as the use of the military instrument by states. This module aims to introduce students to an elementary comprehension of war as a form of politics. A philosophical approach will be taken towards an exposition of general theories of war, as well as land, air, sea, guerrilla and nuclear warfare. It will round off by inquiring whether war studies should necessarily encompass human security today. In this way, the field becomes open to Critical Theory and Postmodern perspectives as well. Students are strongly encouraged to read PS2237 Introduction to International Relations before signing up.
PS4218/EU4228 - European Foreign Policy
Units: 5
Prerequisite(s):
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS with a minimum GPA of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS, or 28 Units in SC, or 28 Units in GL/GL recognised non-language modules, with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): EU4228
Cross-listing(s): EU4228
The European Union is often viewed as an economic superpower but a military pygmy. This module aims to provide students with tools to evaluate whether the EU, as a non-state actor, can have a coherent and effective foreign policy. It considers theories and debates concerning the institutionalisation of the EU’s Common Foreign and Security Policy (CFSP), and includes case studies of EU objectives and actions on selected issues (international trade, ethics, human security), in selected regions (Eastern Europe, the Middle East, Asia and Africa), and in relations with international organisations such as the UN.
PS4226 - Emerging Markets and Economic Governance
Units: 5
Prerequisite(s):
Cohort 2011 and before:
- Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS with a minimum GPA of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
- PS2237, PS3238 and PS3257.
Cohort 2012 onwards:
- Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS or 28 Units in GL/GL recognised non-language modules with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
- PS2237, PS3238 and PS3257.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module offers a close study of emerging markets as rising powers that shape the governance of international economic exchange. The module is organized around two core questions: where are the emerging economies, and why are they important? The course emphasizes a dynamic definition of emerging markets that reflects the ongoing “power shift” in the global economy, including but not limited to countries such as Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa. The module takes an interdisciplinary approach, drawing on political science and economics scholarship to examine emerging markets in international trade and investment, global financial governance, and foreign aid.
PS4231 - Social Theory and International Relations
Units: 5
Prerequisite(s):
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS or 28 Units in EU/LA [French/German] recognized modules with a minimum GPA of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012-2014:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS, or 28 Units in SC, or 28 Units in EU/LA [French/German] recognized modules with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2015 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS or 28 Units in SC or 28 Units in EU/LA [French/German/Spanish] recognized modules with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): PS3880B
Cross-listing(s): Nil
Critical international relations theory argues that the social structures of the international system are the product of human interaction in specific historical circumstances. It also argues that these structures contribute to oppressing much of the world's population. How did these oppressive structures emerge, and why do they persist? Who gains from them and how do they maintain their privileged position? This module will explore such questions by examining major traditions in critical theory, including Marxism, constructivism, post-modernism, and critical feminist theory and applying these theories to issues in international relations.
PS4234 - Identity Politics
Units: 5
Pre-requisite: (a) Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS or 28 Units in GL/GL recognised non-language modules, with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This is a course that explores the origins, reproduction, and effects of social identity from a variety of perspectives. The sources of identity that are investigated include the self, group, society, and state, as well as their more complicated combinations. The identities whose origins, maintenance, and effects we study are nation, ethnicity, gender, religion, sexuality, and race. The approaches we take to make sense of identity politics include writings in political science, social psychology, sociology, history, anthropology, and cultural and post-colonial studies.
PS4235 - War Termination and the Stability of Peace
Units: 5
Pre-requisite: Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS or 28 Units in GL/GL recognized non-language modules, with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This course examines some of the issues and challenges pertaining to the causes of, and the conditions associated with, conflict continuation and termination. The course surveys some of the major theoretical approaches to war termination and examines how some of the major wars have ended in the past century. In addition, this course also examines how other forms of conflict in the international system, such as civil wars, insurgencies, international rivalries and terrorism, have terminated. Lastly, policy and operational challenges linked to war termination are also examined.
PS4239 - Seminar in International Relations of Southeast Asia
Units: 5
Pre-requisite: Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS, with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This advanced seminar explores the international politics of Southeast Asia using new and innovative theories from International Relations (IR). Southeast Asia is at the crossroads of a range of contemporary dynamics: from US-China power-shifts, and South China Sea disputes, to democratic transitions (Burma) and populist authoritarian rollbacks (Philippines). The scholarly study of Southeast Asian IR has not kept pace with the region, however. This module draws on IR practice theory, international political sociology, feminist theory, emotions theory, and diplomatic history to examine how colonialism, class, ethnicity, gender, emotions, domestic politics, regime types (democracy/authoritarianisms) etc., shape Southeast Asian IR.
PS4311 - International Relations in Political Thought
Units: 5
Pre-requisite:
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS or 28 Units in EU/LA [French/German]/recognised modules, with a minimum GPA of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012 - 2014:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS or 28 Units in EU/LA [French/German]/recognised modules, with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2015 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS or 28 Units in EU/LA [French/German/Spanish]/recognised modules, with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): PS4213 International Political Theory
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module explores topics of international relations as they are treated in classical political thought. Topics include: nature and purpose of political order; causes of war; sovereignty and self-determination; balance of power, diplomacy, international law, family of nations, and the transformation of international political community. These topics are examined in the context of key international relations distinctions: inside/outside; universal/particular; and system/society. Particular attention will be given to identifying patterns of continuity and change that explain how these topics have been understood historically.
PS4882 - Topics in International Relations
Units: 5
Prerequisite(s):
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS with a minimum GPA of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module will offer special topics in international relations. Students should check the topics that are on offer in a given semester before enrolling in the appropriate section of the module.
PS4882A - Globalisation, Security and the State
Units: 5
Prerequisite(s):
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS with a minimum GPA of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS, or 28 Units in SC, or 28 Units in GL/GL recognized modules with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This seminar studies the effects of globalization on security. It considers the proliferation of weapons of mass destruction, terrorism, crime, environmental degradation, migration, public health, and other issues. How do states and non-state actors deal with transnational threats? What are the implications of these issues for traditional understandings of sovereignty and non-intervention? What is the role of international institutions and global civil society in responding to these threats?
PS4882D - Politics in Global Migration
Units: 5
Prerequisite(s):
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS with a minimum GPA of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS or 28 Units in GL/GL recognized non-language modules, with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This seminar examines the causes and consequences of transnational migration, a complex and little understood aspect of globalisation. How have governments and international organizations responded to mass population movements? How has transnational migration been treated as a political, economic, security, and human rights issue? What are the gender aspects of migration? We will explore these topics through historical and contemporary perspectives on migrants and refugees. We will consider a wide range of sending and receiving countries, focusing on states and movements in Southeast Asia.
PS4882E - Arms Control
Units: 5
Prerequisite(s):
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS with a minimum GPA of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS or 28 Units in SC, or 28 Units in GL/GL recognized non-language modules, with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This seminar will provide an in-depth examination of issues related to Weapons of Mass Destruction (WMD) and the international institutions designed to reduce the threat of these weapons. It will examine the technology behind WMD, analyze the development of international arms control institutions, and consider emerging arms control issues such as the threat of terrorists using WMD, the weaponization of space, nuclear smuggling and small arms control.
PS4882F - The Politics of International Trade
Units: 5
Prerequisite(s): PS2237, PS3238, PS3257
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS with a minimum GPA of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS, or 28 Units in SC, or 28 Units in GL/GL recognized non-language modules, with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module is designed as a research seminar for upper-level Political Science majors. Students will survey the major areas of scholarship in international trade politics. Each student will also develop and complete a semester-long research project on a topic to be decided in consultation with the instructor. This module strengthens the international relations program of the department.
PS4882G - Politics of International Economic Relations
Units: 5
Prerequisite(s):
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS with a minimum GPA of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS or 28 Units in GL/GL recognized non-language modules, with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module provides students with a greater understanding of the scientific study of the politics of international economic relations, in particular the politics of trade. The module emphasizes current academic scholarship on a number of substantive topics. These topics include the distributional consequences of trade and the domestic sources of trade policy, the design and evolution of global trade governance under the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade and World Trade Organization, the politics of preferential trade agreements, as well as the relationship between trade, international investment, exchange rate regimes, and economic development.
PS4882H - Food Politics
Units: 5
Prerequisite(s):
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS with a minimum GPA of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS or 28 Units in GL/GL recognized non-language modules, with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
What you eat can kill you. We all know that. Less well understood is that what you eat can kill many others, too. This module explores the politics of food from the local grocery store to the international trade in grain, sugar, and cacao. Topics to be covered include food production safety, labelling, and nutrition; environmental concerns relating to energy consumption and waste disposal; the politics of fast food; organic farming and sustainable agriculture; genetically modified foods; the ethics of animal care; vegetarianism, and the politics of hunger and malnutrition.
PS4882I - International Society
Units: 5
Prerequisite(s):
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS with a minimum GPA of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS or 28 Units in GL/GL recognized non-language modules, with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
International society is classically defined as a group of states that are associated in respect of common norms, values, and institutions. This module explores the historical development of international society, from its Christian and European origins to its gradual expansion into a genuinely global political arrangement. It also explores fundamental institutions, such as war, diplomacy, international law, great powers, and the balance of power. Particular attention will be give to the role of culture in international society (western and non-western), theories of empire, the revolt against the west, and alternatives to a society of states.
PS5314R - Seminar in International Relations
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): IZ5102, PS5208, PS6208, PS6301A, PS6401
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This is a core module in international relations which also challenges post-graduate students to begin original research in the subfield. Masters and Ph.D. students who specialise in international relations will be required to read this module. The module will introduce to students important and influential theories on international relations, including realism and liberalism, that attempt to explain cooperation and conflict among nations. Students will also be exposed to some of the important methods of analysis - such as case studies, formal modeling, and statistical analysis - that help distinguish the current study of international relations from that of previous eras. Important approaches, such as constructivism and rational choice, will also be discussed. Under the instructor's guidance, students will undertake an academic-quality presentation to the class and write a paper which proposes in detail an original research project in international relations.
PS5408R - International Institutions
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): PS5404, PS6404
Cross-listing(s): Nil
There are various types of international institutions with implications for international politics, security, and economic affairs. In this regard, the module examines issues such as transnationalism, complex interdependence, regime theory, neo-functionalism, and neo-liberalism. Apart from examining global institutions like the United Nations, the World Bank, the International Monetary Fund, and the World Trade Organisation, special emphasis is placed on institutions that have direct impacts on international relations in Asia, including ASEAN, APEC, ASEAN Regional Forum, ASEM, and SAARC. Students interested in International Relations are encouraged to read this module.
PS6402 - International Conflict and Security
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
The main emphasis of the module will be to explore major theoretical concerns in international conflict. The connection between basic theories about the nature, determinants and dynamics of international conflict will be analysed. Protracted conflicts like the ones in the Middle East, South Asia and Northeast Asia will be studied in depth. Conflict termination strategies and the role of track two diplomacy and third party mediation will also be explained. The seminar will also discuss other non-traditional security issues, including environmental protection, terrorism, and migration, in light of theories on conflict resolution and cross-country cooperation. Students interested in International Relations are encouraged to read this module.
EU3228 - The EU and ASEAN in the World
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): PS3251
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This is a module that studies and compares the external relations of two emblematic regional organizations - in Europe (the EU) and Southeast Asia (ASEAN). A common theoretical literature base is examined and tested against both the EU and ASEAN, using concepts such as "integration", "regionalism", "international organisation", "security communities" and "inter-governmental bargaining" to explain the genesis, functions and utility of ASEAN and the EU. The focus is on the international bargaining, diplomacy, trade negotiations and relations of the EU and ASEAN with the great powers (especially the US, China, Japan, Russia) and with each other. Some background in Asian studies, European studies, International Law, or International Relations would be helpful to the prospective student.
GE2222 - Politics and Space
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module introduces students to the major thematic concerns that have traditionally shaped political geography as a sub-discipline. It also allows students to engage with emerging issues that are likely to become focal points in shaping future debates among political geographers. The aim of the module is to explore the co-constitutive relationship between politics and space. As the political organization of society has spatial consequences, so too does geography influence our understanding of political relationships. These relations are negotiated and contested in multiple ways that cut across different locations, scales, and temporalities. Accordingly, we will examine political concerns, disputes, accommodations, and consequences from a geographical perspective, where students can expect to acquire a critical appreciation for the historical trajectories and evolving implications of states, sovereignty, territoriality, nationalism, colonialism, democracy, ethnic conflict, policing and crime, terrorism, war, environmental justice, and political activism.
HY4209/EU4226 - Imperialism and Empires
Units: 5
Pre-requisite:
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in EU/ LA [French/German]/recognised modules, with a minimum GPA of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012-2014:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in EU/ LA [French/German]/ recognised modules, with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2015 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in EU/ LA [French/German/ Spanish]/recognised modules, with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): EU4226
Cross-listing(s): EU4226
This module will explore in depth, in seminar format, problems in a selected area or aspect of modern imperialism. It will examine in closer focus a particular empire (British, Dutch, French, Portuguese, Spanish, and American) with particular reference to Asia and to Asian interaction with Europe and America. Common themes will include subaltern history, economic development, challenges to imperial control, and explanations and arguments about imperial decline.
HY4225 - Ideological Origins of US Foreign Policy
Units: 5
Pre-requisite:
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in HY, or 28 Units in SC with a minimum GPA of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in HY, or 28 Units in SC, or 28 Units in PS, with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
Beyond international circumstances, domestic politics and personalities, a vital key to understanding the complexities of United States’ foreign policy is through its ideological dimensions. This module will enable students to explore these ideological threads through both seminal documents and scholarly discourses. The module will be taught through both lectures and student presentations. Students will read, present and write on important documents such as John Winthrop’s City upon a Hill, George Washington’s Farewell Address, the Monroe Doctrine, Woodrow Wilson’s Fourteen Points, and George Kennan’s containment policy.
JS3223 Japan and the Asia-Pacific Region (International Relations subfield)
Units: 4
Prequisites: Nil
This course aims to develop students' understanding of Japan's external relations with other nations in Asia and the Pacific. Students will learn about the most contemporary issues in Japanese external relations, place them in a modern historical context, and analyse them with theoretical frameworks and political concepts. The topics include the Japan-US security alliance, historical problems related to Yasukuni Shrine and history textbooks, ODA and PKO, territorial disputes, as well as Japan's commitment to regional institutions in the Asia-Pacific.
JS4224 - Japanese International Relations
Units: 5
Pre-requisite:
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in JS or 28 Units in PS, with a minimum GPA of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in JS or 28 Units in PS or 28 Units in GL/GL recognised nonlanguage modules, with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module aims to promote the better understanding about Japan's foreign policy and international relations. The module consists of three analytical focuses: defence and security policies, foreign economic policy and regional and multilateral institutions. The first section highlights major features of Japan's defence and security policies including the recent changes in Japan's security environment in the Asia Pacific region and their impact on Japan's defence policy approaches. The second section focuses on the characteristics of Japan's policies of international trade and foreign aid. This section also discusses the domestic system in the context of Japan's foreign economic policy and highlights how the Western critics regarded the issue as problematic. The third section examines Japan's approaches to regional institutions such as APEC, ARF, ASEAN+3, and the G-8 Summit Meeting and United Nations, with focuses on its approaches and diplomatic activities in each case. Although this module highlights more empirical cases of Japanese foreign policy, it also introduces some theoretical debates as well.
PP5181 - State Fragility and Peacemaking
Units: 4
Pre-requisite:
This module is open to upper-level NUS undergraduates. If so, undergraduates should sufficient background in political science and international relations – for example they are single or double major in political science/IR or have a declared minor in political science/IR. If the students
are from a liberal arts background, such as from Yale-NUS, they should have a declared major in Global Affairs or Politics, Philosophy and
Economics.
For graduate students, students registering for this module should ideally have an undergraduate degree in government, political science, international relations or Law. If the undergraduate degree is general, they should have a declared undergraduate major/minor in government, political science and/or international relations or have a basic background in political science or IR.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
Fragile and failed states pose unique problems to the international community. From the 1990s, wars in and among failed states have killed and displaced millions. In an increasingly interconnected world, internal insecurity fundamentally undermines international security. This module focuses on understanding the main drivers of state fragility and the impact on global security. In understanding the root causes and consequences of state fragility, students will work through appropriate and practical policy responses. The module draws on contemporary case studies of contested states and explores the issues through the lenses of political science, international relations, history, geography, sociology and public policy.
SC4882B - Citizenship, Nation and Globalization
Units: 5
Pre-requisite:
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in SC with a minimum GPA of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in SC, or 28 Units in PS, or 28 Units in GL/GL recognised non-language modules with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): SC4215B Citizenship, Nation and Globalization
Cross-listing(s): Nil
The concept of citizenship has been understood as the mechanisms through which the individual is linked to the nation, involving a variety of processes, such as rights, culture, or race. There are new claims that with globalization, there has been the re-definition of the idea of the citizenship and the nation, leading to new concepts such as flexible citizenship and de-territorialized nation-states. This course will examine how that movement of people, GPAital, and ideas are affecting citizenship, and how this affects the relation between state and society. This module is mounted for students throughout NUS with interest in the concept of citizenship.
SC4883 - Selected Topics in Law and Justice
Units: 5
Pre-requisite:
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in SC with a minimum GPA of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in SC, or 28 Units in PS, with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): SC4216 Selected Topics in Law and Justice
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module aims to increase students' breadth of empirical knowledge and the depth of their theoretical understanding on issues of law, justice and society. With urbanization and industrialization, modern societies have increasingly depended upon law to regulate the behaviour of its members and the activities of its institutions. In contemporary Singapore society, law underpins social policies from housing to marriage, political behaviour and economic activities. Among the wide variety of significant topics are policing theories, state violence and social justice, crime and punishment to the legal profession. This module is mounted for students with interest in law and justice.
SE5294R - The Politics Of Environment in SE Asia
Units: 5
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
The growth and development that has taken place not only in the Southeast Asian region but also in the rest of the world is commonly viewed to have a negative impact on the environment in the region. Is it necessarily true? Are there positive effects as well? This module will evaluate the link between the developmental process and the environment including an analysis of the problems, the proposed solutions, and the actual policies implemented. The module provides not only a Southeast Asian perspective on the environmental and the developmental issues facing the region, but also a geographical outlook. This emphasises the sharing of natural areas and resources among nation-states and their peoples in Southeast Asia given the historical background of the region with its impact on national borders and the composition of both the population and society. The outcome on nature and society relations seen in Southeast Asia reflect conditions specific to the region and its geography. This module is aimed at understanding both these specific conditions and the wider as well as external factors that have an impact on environment in Southeast Asia.
SN3223 - International Relations of South Asia
Units: 4
Pre-requisite: Nil
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module focuses on the International Relations of the South Asian region. It looks at intra-regional relations, the impact of domestic politics on foreign policy, issues of conflict and cooperation and the role of external powers in the region. The foreign policy behaviour of India and Pakistan in particular will be considered. Key issues like the Kashmir conflict, nuclearization of South Asia and terrorism will be explored. The increasing significance of the South Asian region in the emerging global order, regional integration and inter-regional relations will also be analysed.
GL4882A - Development and the Globalisation of Food
Units: 5
Pre-requisite: Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in GL or GL recognised non-language modules or 28 Units in PS with a minimum GPA of 3.2 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
The module will be organized around the following four topics. First, the vision of agriculture found in early development thought; second the structural transformations of agriculture in the twentieth century in terms of production and trade; third, an examination of states that have resisted the globalizing tide in order to determine whether their domestic policies qualify as “development”; and finally the possibility of decoupling development and globalization.
GL4882B - Contested Globalisation: Resistance and Resilience
Units: 5
Pre-requisite: Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in GL or GL recognised non-language modules or 28 Units in PS with a minimum GPA of 3.2 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This interdisciplinary module examines the ways in which globalisation has provoked resistance as well as resilience. Global forces are often presented as inevitably and overwhelmingly structuring local actors and processes. But globalisation remains widely resisted in various ways. By drawing on materials from global studies, history, sociology, economics and political science, the class interrogates the varied local sources of and resistance to globalisation in different issue areas, ranging from health and the environment to migration and development. It problematises key concepts related to global processes and places them in the context of crucial debates about globalisation.
GL4882C - The Politics of Global Finance
Units: 5
Pre-requisite: Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in GL/GL recognised non-language modules, or 28 Units in PS with a minimum GPA of 3.20, or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module introduces Global Studies students to the conceptual and substantive debates about the politics of global finance within Global Political Economy (GPE). Starting with a history of global finance and its social foundations, the module focuses on four dominant themes; financialization, financial crisis, transnational governance and regulation, and financial intransparency.
GL4882D - Global Corporations and Power
Units: 5
Pre-requisite: Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in GL/GL recognised non-language modules, 28 Units in PS, with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
Global corporations now shape public life in countries across the world. Besides influencing governments and international organizations, they also directly operate services which were once the domain of government. This module investigates corporations as actors involved, often informally, in emerging configurations of power. Topics to be addressed include the roles of corporations in international financial institutions, in advising governments, in delivering overseas assistance, in writing treaties, and in otherwise participating in public life.
GL4883A - Conflict and Natural Resources
Units: 5
Pre-requisite: Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in GL or GL recognised non-language modules or 28 Units in PS with a minimum GPA of 3.2 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module examines the role of natural resource endowments and scarcity in national and international conflicts. The course begins with a review of causes of conflict and develops an understanding of how these causes may be linked to nautral resource endowments. We then explore how constraints on natural resources such as water and fertile soil increase the potential of environmentally linked violence. Students will explore not only conflict theory, concepts of greed and grievance, and scarcity, but also technical aspects of global environmental change. Finally, the class will explore potential conflict resolution approaches.
GL4883B - Climate Justice
Units: 5
Pre-requisite: Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in GL or GL recognised non-language modules or 28 Units in PS with a minimum GPA of 3.2 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
Climate change represents an unprecedented challenge to our political institutions, social norms, and even our theoretical concepts. Since the effects of climate change will be felt everywhere and for hundreds of years, it creates concerns about global and intergenerational justice, both singly and in combination. This module will explore these issues, discussing the ways in which climate change impacts and responses may be normatively criticized or justified, especially in contexts where considerations of justice must be balanced or traded off. To illustrate, we will also consider the normative issues surrounding resilient and sustainable development.
GL4883C - Social Experiences of Disaster
Units: 5
Pre-requisite: Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in GL/GL recognised non-language modules, 28 Units in PS, with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module introduces Global Studies students to social science and humanities approaches to understanding and analyzing environmental disaster. The module furthers students’ understanding of concepts such as vulnerability, resilience, adaptation, environmental justice, sustainability, and the Anthropocene from interdisciplinary, political ecological and ethnographic perspectives.
GL4884A - Glocal Media Worlds
Units: 5
Pre-requisite: Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in GL/GL recognised non-language modules, 28 Units in PS, with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
This module invites students to examine how people engage in global interactions through media. Across the module, students will investigate how media challenges our understandings and experiences of time and distance, and challenges the dichotomy of global versus local worlds. Module topics include: identity, representation, self-representation, media technologies, online social movements, remote labor, transnational family and affective relationships, gaming, and religion.
GL4884B - Living with Infrastructure
Units: 5
Pre-requisite: Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in GL/GL recognised non-language modules, 28 Units in PS, with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
In this module, we will explore the diversity of ways people use infrastructures, and the various social meanings people ascribe them. We will reconsider formal understandings of infrastructure to question how infrastructures perform unexpected roles in society—perhaps as tools for social identity or community formation. We will also pay particular attention to processes and experiences of globalization through infrastructure. For example: how do transoceanic undersea cable networks affect life on their island landing zones? Students will also develop their research skills by working on an ethnography of infrastructure.
GL4885A - International Law and World Politics
Units: 5
Pre-requisite: Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in GL/GL recognised non-language modules, or 28 Units in PS with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): NIL
Cross-listing(s): NIL
This module introduces students to international law and world politics through case studies. It begins by explaining what international law is, and how it is formed, interpreted, and used to advance certain causes or respond to specific events. Cases are introduced to students in their historical, political, and social contexts so that students can grasp not only the salient legal issues in each particular case, but also the larger diplomatic controversies that were at stake in each case and their consequences for international relations today.
GL4888A - Justice and Emerging Technology
Units: 5
Pre-requisite: Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in GL/GL recognised non-language modules, or 28 Units in SC, or 28 Units in PS, with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track. Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module examines moral and public policy challenges presented by emergent technologies that challenge notions embodied in current institutions and theories of what is natural and what is subject to human manipulation, and even create entirely new domains of human activity and interest. These new technologies operate globally and often rapidly, generating consequences far beyond the location of their users. The module studies how social and political institutions-new or old-structure, regulate, develop, and distribute these technologies in accordance with various conceptions of justice.
GL4889A - International Law's Regulation Violence
Units: 5
Pre-requisite: Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in GL/GL recognised non-language modules, or 28 Units in SC or 28 Units in PS, with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours Track.
This module examines how international law regulates the use of different forms of violence. It analyses branches of international law and their relationship to contemporary phenomena of political violence, asking what kinds of challenges the latter pose to the former. In this context, the module explores international law vis-à-vis issues such as (non-)international armed conflict, large-scale collective violence, non-state militancy, counter-insurgency and environmental destruction. Accordingly, topics covered by the module include the international law of armed conflict, international criminal law and international environmental law.
GL4889B - Debates on Human Rights
Units: 5
Pre-requisite: Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in GL/GL recognised non-language modules, or 28 Units in PS, with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
This module examines contentious debates on the origins, meanings and implementations of human rights in order to map out the complexities of the relationship between human rights and politics. We will discuss contending arguments on the definition and historical origin of human rights, analyse the contradictions between different sets of human rights and study the complicated relationship between human rights and political violence.
PS2240 - Introduction to Public Administration
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): PS2210B
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This introductory module defines the scope of public administration in terms of its structures, functions, sectors, and institutions. It familiarises students with some basic concepts used in public administration, including authority, organisation, bureaucracy, accountability, meritocracy, representation, ethics, professionalism, leadership, and decision making. The module also examines major approaches to studying public administration. Practical cases and examples are used in presenting these topics. The module is available to all year 1-3 students at NUS.
PS2241/GEK2012 - Public Administration in Asia
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): GEK2012, GEM2012K, PS2206, PS2211B
Cross-listing(s): GEK2012
The module briefly covers the origins, functions, and contexts of public administration, and various comparative approaches to administrative systems in Asian countries. On that foundation, it then focuses on some of the major administrative issues in Asian countries, including local government and decentralisation, privatisation and public sector reform, ethnic representation, bureaucratic corruption, and administrative accountability. The module can be read by year one to three students across all faculties at NUS.
PS2244/SSA2222 - Public Administration in Singapore
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): SSA2222
Cross-listing(s): SSA2222
This module deals with major themes and issues in public administration with specific reference to Singapore. It covers relevant domains of the city-state’s governance and explores issues such as the relationship between politics and administration, meritocracy and performance, combating corruption, grassroots administration, and e-governance. It also discusses administrative trends and challenges in contemporary Singapore.
PS3243 - Public Sector Organisational Behaviour
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): IF2205, IF3214, PS2205, PS3213B
Cross-listing(s): Nil
Why organizations behave as they do? What explains the creation, change, and prosperity of organizations? Social scientists have risen to the challenge to address these questions. In this module, students will learn the fundamental perspectives in organizational theory and their application to and transformation over time. The discussion pays particular attention to organizational and human behaviors in public sector organizations. As such, it is ideal for students interested in public management and those who aspire to work in the public sector.
PS3246 - Public Ethics and Corruption
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): PS3221, PS3216B
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module examines the question of ethical standards governing the conduct of public officials and the linkage between corruption and governance in Asia and other regions. Attention is given to the causes of corruption and the effectiveness of anti-corruption measures as well as to broader issues of public service ethics and administrative responsibility.
PS3262 - Managing Non-Profit Organisations
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module presents a broad overview of non-profit organisation management. Based on public administration and strategic management theory, it focuses on practical problem-solving ideas. Topics to be considered include:
- shaping an organisation’s vision and mission,
- SWOT analysis,
- decision-making,
- establishing strategic management capacity,
- inter-organisational cooperation and partnership, and
- other management techniques.
PS3271 - Public Policy Making
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): PS2242
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module covers the institutional and procedural dimensions of public policy-making. It introduces theories of policy-making, such as rationality, incrementalism, and policy networks, and it explores how major political institutions-including executives, legislatures, bureaucracies and interest groups-affect the policy-making process. The stages of policy-making, such as agenda-setting and policy formulation, implementation, evaluation and termination, are also considered. Case studies are used to illustrate these complex processes. The module is designed for students who are interested in governance and policy-making and may be considering a career in the public sector.
PS4209 - Public Organisation Theory and Practice
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s):
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS with a minimum GPA of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This is an advanced module on public organisation. It analyses various concepts and theories of organisation and examines critical organisational issues in the public sector. The major theories discussed in the module include the classical, neo-classical, systems, contingency, and critical theories of organisation. It also focuses on specific organisational issues such as decision making, motivation, leadership, administrative ethics, and organisational change with special reference to the public sector. The target students for this module include both honours and postgraduate students in Political Science.
PS4230 - Public Sector Reforms in China
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s):
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS, with a minimum GPA of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS, or 28 Units in SC, or 28 Units in GL/GL recognized non-language modules, with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
Chinese leaders in the reform era face a distinct governance challenge: economic transition requires major revamps in the ways China is amanged while an overhaul of the political system is not a viable option. Against the backdrops, Chinese leaders have carried out substantial reforms in public sector organisations. This module examines the content, rationale, and outcomes of public sector reforms in China. Major topics include reforms on cadre personnel management, public finance, healthcare, education and enterprise systems. It helps students understand the significant role of public sector reforms in China’s transition, and the challenges caused by these reforms.
PS4344 - Artificial Intelligence and Public Policy
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s):
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS with a minimum GPA of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This seminar-style course for political science students explores how AI technologies reshape policy decisions and societal outcomes. It focuses on three critical issues: AI's impact on key public policy concepts like power, accountability, ethics, and bureaucracy; governance and regulation of AI for reliability and trustworthiness; and global responses to AI challenges and opportunities. The course covers theoretical discussions and case studies from the US, China, Japan, the EU, and Southeast Asia. Students will gain a deep understanding of AI's effects on politics, policy, and governance, preparing them for the AI-driven future workplace.
PS4884 - Topics in Public Administration
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s):
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS with a minimum GPA of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module will offer special topics in public administration. Students should check the topics that are on offer in a given semester before enrolling in the appropriate section of the module.
PS4884A - Applying Public Policy Theory
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s):
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS with a minimum GPA of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS, or 28 Units in SC, with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This seminar studies the theory and practice of public policy-making. Topics include alternative ways of framing policy problems, seeking policy alternatives and solutions, designing and implementing policies, and evaluating policy outcomes. Students will apply ideas considered under these topics to problems in economic, welfare, education, environmental, and regulatory policy.
PS5316R - Seminar in Public Administration
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This seminar is designed for graduate students in any subfield of political science. The module examines the intellectual history of public administration and the basic issues that confront it today. The seminar pays particular attention to administrative responsibility and ethics and to the formulation and implementation of public policy. To this end, it will emphasise the nexus of public administration and politics.
PS5503R - Decentralisation and Local Governance
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Students must have a basic proficiency in social science quantitative research.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
The last thirty years has seen a wave of enthusiasm for decentralization, with advocates suggesting its implementation as a remedy to some of the most intractable problems in governance. Yet the anticipated benefits of these reforms have since been distributed unevenly. By engaging cutting-edge empirical and theoretical research from economics and political science, this seminar will examine the promise and pitfalls of decentralization across diverse contexts. Looking across sectors, special attentions will be given to understanding the conditions under which decentralization achieves greater political accountability, improves service delivery, and boosts economic growth.
PS5504R - Development Theory, Policy and Institutions
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module deals with theories, policies and institutions related to socioeconomic development. After introducting the major concepts and dimensions of development, it critically examines the major traditions of development theories (conservative, reformist, radical). It discusses major development policies practiced especially in the developing world. The module also covers alternative institutional choices – the state, local government, private sector and non-government organisation – in carrying out development plans and policies. It may also include recent debates on Asian models of development depending on the lecturer’s interest or preference to cover such models.
PS5505R - Public Administration Theory
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): PS2240 Introduction to Public Administration or its equivalent subject to the approval of the Instructor.
Preclusion(s): PS6504
Cross-listing(s): Nil
The teaching and learning objectives of this module are to examine various administrative theories and their limitations; to explain recent theoretical developments in public administration; and to analyse these theories and issues in relation to practical administrative systems in various regions and countries. The topics covered in this module include theoretical approaches to public organisation; new theories or models of public management; issues of administrative behaviour (e.g., decision making, leadership, ethics, and accountability); limits of administrative theories; and relevance of western theoretical debates to non-western societies.
PS5506R - Globalization and Public Governance
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This graduate module explains how the powerful forces or actors of globalization led to pro-market neoliberal reforms in the nature of state formation and introduced changes in public governance (policy and administration). In particular, it analyses the neoliberal mode of public management, known as the reinvention of new public management (NPM) model. The module examines major elements of NPM-type reforms (e.g. privatization, outsourcing, public-private partnership, managerial autonomy, and financial decentralization) in East and Southeast Asia. It evaluates the impact of globalization-led neoliberal reforms on democracy, citizen-administration relations, and corruption by using a politic-economic perspective on globalization, state formation, and governance.
PS6505 - Development Policy and Administration
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
The teaching and learning objectives of the module are to introduce theories of development; to explain development policies and puzzles; to examine major current challenges faced by developing nations in Asia, Africa, and Latin America; and to identify viable development alternatives. The major topics will include development concepts and theories, sectoral development policies, institutional reforms for development, role of government and non-government organisations in development, development dilemmas and challenges, and future direction of development.
CDE2502 - Cities for All
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
With the world rapidly urbanising, how will our cities ensure a high quality of life to make cities ‘liveable’? What is liveability and how do we envision it? This course addresses key issues such as housing, accessibility, health and ageing, conservation, and culture to analyse how social structures affect and extend within the built environment. We will explore the ways in which these structures and processes manifest within the urban context to understand how we can further develop sustainable software, hardware, and ‘heartware’ that contribute to an equitable, liveable city with a high quality of life for its citizens
CDE3505 - Planning and Governing Cities
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
The issues that cities face are constantly evolving, and the way in which we address these issues must evolve alongside them. Singapore’s planning framework was developed in a context that differs from that of today where we now face novel, complex issues such as an ageing population, climate change, and sustainability. How will we modify our approach to planning to address these issues? This course introduces students to how Singapore engages with urban challenges that address the Integrated Master Planning & Development and Dynamic Urban Governance systems within the Liveability Framework through a data-driven, innovative, systems approach.
GL4883B - Climate Justice
Units: 4
Pre-requisite: Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in GL or GL recognised non-language modules or 28 Units in PS with a minimum GPA of 3.2 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
Climate change represents an unprecedented challenge to our political institutions, social norms, and even our theoretical concepts. Since the effects of climate change will be felt everywhere and for hundreds of years, it creates concerns about global and intergenerational justice, both singly and in combination. This module will explore these issues, discussing the ways in which climate change impacts and responses may be normatively criticized or justified, especially in contexts where considerations of justice must be balanced or traded off. To illustrate, we will also consider the normative issues surrounding resilient and sustainable development.
GL4883C - Social Experiences of Disaster
Units: 4
Pre-requisite: Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in GL or GL recognised non-language modules or 28 Units in PS with a minimum GPA of 3.2 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module introduces Global Studies students to social science and humanities approaches to understanding and analyzing environmental disaster. The module furthers students’ understanding of concepts such as vulnerability, resilience, adaptation, environmental justice, sustainability, and the Anthropocene from interdisciplinary, political ecological and ethnographic perspectives.
GL4884B - Living with Infrastructure
Units: 4
Pre-requisite: Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in GL or GL recognised non-language modules or 28 Units in PS with a minimum GPA of 3.2 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
In this module, we will explore the diversity of ways people use infrastructures, and the various social meanings people ascribe them. We will reconsider formal understandings of infrastructure to question how infrastructures perform unexpected roles in society—perhaps as tools for social identity or community formation. We will also pay particular attention to processes and experiences of globalization through infrastructure. For example: how do transoceanic undersea cable networks affect life on their island landing zones? Students will also develop their research skills by working on an ethnography of infrastructure.
GL4888A - Justice and Emerging Technology
Units: 4
Pre-requisite(s): Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in GL/GL recognised non-language modules, or 28 Units in SC, or 28 Units in PS, with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module examines moral and public policy challenges presented by emergent technologies that challenge notions embodied in current institutions and theories of what is natural and what is subject to human manipulation, and even create entirely new domains of human activity and interest. These new technologies operate globally and often rapidly, generating consequences far beyond the location of their users. The module studies how social and political institutions-new or old-structure, regulate, develop, and distribute these technologies in accordance with various conceptions of justice.
SC4203 - Sociology of Organizations
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s):
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in SC with a minimum GPA of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in SC, or 28 Units in PS, or 28 Units in GL/GL recognised non-language modules with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module deals with exciting theoretical and practical issues in the sociology of organizations. Some of the questions addressed are
(1) What kind of 'animal' is this creature called organization?
(2) What are its key characteristics: structure, culture, environment?
(3) Who created this 'animal', or what goals, and with what strategies to achieve the goals set?
(4) How does it influence the orientation and action of participants?
(4) Is democracy possible within organizations?
This module is mounted for students with interest in one of the most important social entities influencing key aspects of social, political, and economic life in modern societies.
PS2203/EU2203 - Ancient Western Political Thought
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): PS2231, EU2218, PS2201B, PS2218, EU2203
Cross-listing(s): EU2203
This module explores basic political ideas from the ancient Greeks and Romans from the emergence of the polis to the collapse of the empire, including the ideas of justice, law, democracy, and politics itself, through the study of original works by Thucydides, Plato, Aristotle, St. Augustine, and others. It also considers how these ideas shaped medieval and early modern political thought.
PS2204/EU2204 - Modern Western Political Thought
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): EU2204
Cross-listing(s): EU2204
This module explores major political ideas and concepts from the modern Western tradition. Key political constructs such as power, authority, justice, liberty and democracy are examined in intellectual and historical context. Reading Thomas Hobbes’s Leviathan and John Locke’s Second Treatise on Government, among other influential writings, students will be exposed to the broader themes and ideas that have shaped political life in the West since 1600.
PS2231 - Western Political Thought
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): EU2218, PS2201B, PS2218
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This course introduces students to the major works of Machiavelli, Hobbes, Locke, Adam Smith, Rousseau, and Nietzsche. These thinkers help us to understand the sources of current and competing beliefs about social and political life. So, while we seem to cherish ideas such as freedom, progress, and creativity, we are also troubled by the impact of these ideas on our beliefs in the importance of culture, tradition, and community. This course would be helpful to students interested in the political implications of globalization and the new economy.
PS2232 - Islamic and Hindu Political Thought
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): PS2202B, PS3218
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module is divided into two parts, namely, Hindu Political Thought (HPT) and Islamic Political Thought (IPT). HPT will expose students to the rich tradition of competing ideas that shape the evolution of Hindu political thought and philosophy and will cover the major ideas of classical Hindu epics such as Kautilya and Manu. IPT will help students understand the Islamic worldview in general and the Islamic conception of political theory in particular, and will deal with topics such as principles and sources of Islamic thought and governance of Islamic states, according to the primary sources of Islamic Law, the Qur’an and Sunnah. This module is suitable for beginning students interested in normative political theory in eastern civilisations.
PS2233/GEK2024 - Political Ideologies
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): EU3208, PS2203B, PS3210, GEK2024
Cross-listing(s): GEK2024
This module begins with the examination of various strands of liberalism, including liberal versions of communitarianism, and then proceeds on that basis to survey various significant reactions to liberalism. In addition to communism and fascism, the module will also examine the ideological challenges to liberalism from radical/ militant Islamism and the advocates of so-called “Asian values.” This is an introductory module and is designed for any beginning student with an interest in the theoretical approach to the study of competing political belief systems.
PS2256/GEK2043 - Politics on Screen
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): GEK2043
Cross-listing(s): GEK2043
The module examines representations of politics in film and television and considers the ways in which they become politically controversial as objects of regulation and censorship, economic commodities or projections of cultural ‘soft power’. It also considers the reflexive potential of film and television to comment their socio-political role as well as on their own representation of politics. The module explores these themes in a variety of cinematic and televisual ways of representing politics, including documentaries, dramas, historical re-enactments, and comedies.
PS2258 - Introduction to Political Theory
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
Political Theorising considers basic questions about government, citizenship, equality, justice, rights and the use of force. This module investigates these and related questions by reading and discussing classic and contemporary sources of different kinds, from letters, stories, and manifestos to systematic works of philosophy. By engaging with some of the most readable and interesting of these writings, once can learn how such questions have been answered in different times and places, as well as one’s own.
PS2266 - Politics, Music and Society
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): PS3266
Cross-listing(s): Nil
Music has been politically important since ancient times in all cultures. In ancient Athens, Plato wrote that ‘when the mode of music changes, the walls of the city tremble’, and in traditional China, Confucians and Legalists engaged in extended controversy over the social desirability of music. Students will be asked to read theoretical writings on music and politics by these and other thinkers (including Rousseau, Nietzsche, and Adorno). No prior musical experience is required; the course is aimed at musicians and non-musicians alike. The focus is on the meaning of music and not its technical aspects.
PS2300 - Humanity between Animals and Robots
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
Human beings have long described ourselves as something more than animals and more than thinking machines: more rational, intelligent, sociable, creative, or capable of love. What is distinctively human changes with the comparison: the ancients thought that unlike animals, human beings were capable of reason and speech; the philosopher John Searle argued that computers could not really understand human speech. Developments in both animal studies and in artificial intelligence have challenged our assumptions about humanity from both ends. Do we still think of humanity as more than animals and thinking machines, and what does the more consist of, if anything?
PS3215 - Equality and Justice
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): YSS3355
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This course asks questions about the relationship between equality and justice, e.g. is it unjust for a society to be unequal? Unequal in what way? How do our political systems reproduce relations of equality or inequality? Do we have a responsibility to compensate for some inequalities, and which ones? We will read "classic" contributions from the contemporary debate on egalitarianism (e.g. from John Rawls, Robert Nozick, Michael Walzer and others), as well as consider the application of theories of in/equality to current affairs in Singapore and elsewhere.
PS3232 - Democratic Theory
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module introduces students to the core tenets of modern democratic theory in the context of real-world politics. Tracing democracy’s historical evolution in the writings of Aristotle, Locke, Rousseau, Tocqueville, and Schumpeter among other prominent thinkers, this module examines the complex web of constitutional structures and institutions vital to its success. This module also examines various problems endemic to democracy as well as possible solutions to these problems by more recent democratic theorists such as Robert Dahl and Benjamin Barber. The course is intended for political science majors and students with a background in political science.
PS3256 - Politics and Film
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): NIL
Cross-listing(s): NIL
Film and politics have always been closely related. Film-makers have created dramas, comedies, satires, and works of propaganda in order to comment on politics and advance political causes. But film also has off-screen effects, so we can talk about the politics of film as well as politics on film. The course combines concepts from film studies and political theory to explore the different ways in which film can be politically important, covering some of the most famous political films ever made from the beginning of the twentieth century all the way up to the contemporary era.
PS3259 - American Political Thought
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This modules examines the American political tradition, focusing on the ideas that inform America’s unique system of governance during the past two centuries—revolution, self-determination, constitutional government, the separation of powers, the legal protection of basic moral rights, federalism, slavery, equality, and civil disobedience. Students will study the writings of America’s most important political thinkers including Madison, Hamilton, Jefferson, Lincoln, Emerson, Thoreau, and Martin Luther King.
PS3260/GEK3005 - Politics and the Visual
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): GEK3005
Cross-listing(s): GEK3005
This module explores the many forms of relationship between politics and visual culture. From the ancient world to the present, politics, whether formal or popular, has had a visual dimension. Politicians have been concerned to control their appearance; various media (from painting to theatre to television to the internet) have been used to both serve and defeat this goal. The module offers surveys the relationship between politics and visual culture and allows students to engage with contemporary issues surrounding politics, film, and digital culture.
PS3267 - German Political Thought
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module studies German political thought since the Enlightenment. Reading selections in English translation from the political writings of nineteenth-century luminaries such as Hegel, Marx and Nietzsche together with important twentieth-century thinkers such as Weber, Heidegger and Habermas, it introduces students to the major thinkers, ideas and problems of the modern German political tradition. Among the topics covered are the intellectual origins of German idealism and communism, Weimar politics, Nazism, the Frankfurt School and Habermas’s theory of deliberative democracy.
PS3269 - Medieval Western Political Thought
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): PS2204/EU2204
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module interrogates major concepts and institutions of Latin Christendom in the 12th-15th centuries. The module begins by examining the Greek, Roman, and Biblical foundations of medieval thought, followed by a series of conceptual issues. Topics include the nature of temporal and spiritual power, and the relation between them; different kinds of law—divine natural, and human—and their bearing on human relations; theories of medieval government; notions of community and representation, and the relation of state and individual. The module will conclude by reflecting on what the modern world has inherited from the Christian Middle Ages.
PS3310 - Populism and the Future of Democracy
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
Populists challenge democracy worldwide, disrupting domestic and international order. Despite its prevalence, populism remains difficult to define, let alone respond to. This course explores populism through the lenses of philosophy, politics, and economics. Using theoretical works and case studies, we will address key questions: What is democracy, and how does it decline? What is populism, and how does it relate to democracy? How do populists behave in power? Why do voters support populists? And how should states respond to populism?
PS3880A - Modern Chinese Political Thought
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module considers important transitions in Chinese political thought from the late nineteenth to the early twentieth centuries. We will survey the growth of critical consciousness from 1890 to the May Fourth Movement, the rise of and reactions to Communism, and the revival of Confucianism in the 1970s and after. We will consider such questions as: what concerns preoccupy Chinese political thinkers of this period? What is the value of Chinese traditions for thinking critically about China’s political future? How can “Chinese” political thought be understood to have global relevance?
PS4201 - Contemporary Political Theory
Units: 5
Prerequisite(s):
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS or 28 Units in EU/LA
[French/German]/recognised modules, with a minimum CAP of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012 -2014:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS, or 28 Units in SC, or 28 Units in EU/LA
[French/German]/recognised modules, with a minimum CAP of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2015 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS, or 28 Units in SC or 28 Units in EU/LA
[French/German/Spanish]/recognised modules, with a minimum CAP of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
In this module, students will investigate political-theoretic responses to one or more of the following contemporary issues: economic, racial, and gender inequality; political and economic power; the environmental crisis; the rise of authoritarianism; and questions of rights and liberties. Course content will vary according to instructor expertise. The overall goal will be to connect critical and positive theorizing to our political world so that we deepen our political education.
PS4211 - Political Theology
Units: 5
Prerequisite(s):
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS or 28 Units in GL/GL recognised non-language modules, with a minimum CAP of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
Political theology is a mode of inquiry that interprets politics in the context of theological concepts and categories. This module focuses on Christian theological debates, in the late medieval and early modern periods, and considers their impact on the vocabulary of contemporary politics and international relations. Representative topics include: state sovereignty, political rule, extra-legal action, and international order. In recovering this theological inheritance this module dispels widely held myths about the origins of this vocabulary and reinterprets canonical figures in this light. In doing so, it challenges the narrative of progressive secularisation that dominates modern Western political and international thought.
PS4213 - International Political Theory
Units: 5
Prerequisite(s):
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS or 28 Units in EU/LA [French/German]/recognised modules with a minimum CAP of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012-2014:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS or or 28 Units in EU/LA [French/German]/recognised modules, with a minimum CAP of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2015 onwards:
Completed 80 Units in PS or 28 Units in EU/LA [French/German/Spanish]/recognised modules, with a minimum CAP of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): PS3203B
Cross-listing(s): Nil
The issue of morality in international politics is frequently treated as marginal to the contemporary concerns of states in their international relations. Developments such as the Nuremberg Trials, the Cold War, the African Famines of the 1980s, the Genocides in ex-Yugoslavia and the emergence of wrangles over resource exploitation and environmental pollution call attention otherwise. This module equips the student with the conceptual tools and frameworks with which to comprehend and make informed decisions about these cross-boundary ethical complexities. Both Political Science majors and non-Political Science students will find this a useful supplement to studies of international politics and philosophy.
PS4215 - Politics of Non-Violence
Units: 5
Prerequisite(s):
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS with a minimum CAP of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS or 28 Units in GL/GL recognised non-language modules, with a minimum CAP of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module examines the intellectual foundations, rationale, relevance and practicality of non-violence in the political arena. Reading early arguments for non-violent direct action in the writings of early nineteenth-century thinkers, such as Leo Tolstoy, John Ruskin and Henry David Thoreau, the module analyses the effectiveness of non-violence as a political strategy in Gandhi’s campaign for India’s independence, the American Civil Rights Movement, and Nelson Mandela’s struggle to liberate South Africa from Apartheid. To prepare for this module, it is suggested that students have read PS3233, Political and International Ethics.
PS4217 - Major Political Thinkers
Units: 5
Prerequisite(s):
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS with a minimum CAP of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS with a minimum CAP of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
The Major Political Thinkers series examines the writings and historical contexts of the most important political thinkers throughout the history of political thought. Each module focuses on one or two thinkers, such as Plato, Aristotle, Aquinas, Hobbes, Locke, Marx, Rousseau, Kant, Rawls, and others.
PS4219 - Comparative Political Thought
Units: 5
Prerequisite(s):
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS with a minimum CAP of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS, or 28 Units in SC, with a minimum CAP of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): PS3201B, PS3231
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This course will explore the emerging field of comparative political theory (or CPT) by considering to what extent it stands as a coherent, independent subfield, and what if any are the questions it is specifically poised to answer. Our treatment will be both topical and methodological. We will begin by reading the work of contemporary scholars who explicitly situate themselves within “comparative” as opposed to mainstream canonical political theory, and/or who use comparison as a tool for elucidating particular political problems. In the second part of the course, we will read primary sources that undertake comparative or synthetic perspectives on formulating theory in the modern world, but from self-consciously “indigenous” perspectives.
PS4220 - Rhetoric and Politics
Units: 5
Prerequisite(s):
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS or 28 Units in EL/EN, with a minimum CAP of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS or 28 Units in EL/EN, with a minimum CAP of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
The art of persuasion is central to political activity. Aristotle’s treatise on rhetoric, which analysed legal and political discourse, set the agenda for discussion of the subject until the modern era and remains supremely relevant to politics today. Political theorists and historians of political thought have recently rediscovered the subject of rhetoric and there is a wide array of fresh writing available for students to study. This module will provide invaluable insight into the nature of political speech for all who opt for it and greatly enhance their ability to dissect the language of politics.
PS4229 - The Politics of Knowledge
Units: 5
Prerequisite(s):
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS with a minimum CAP of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS with a minimum CAP of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
Ways of knowing have always been connected with particular forms of political organisation. For example, the idea of an ascending hierarchy of forms of knowledge culminating in the knowledge of the good found in Plato’s Republic also implies a hierarchical social order capped by an elite of ‘guardians’ who have mastered this sequence; the government of Confucian China required a scholarly elite distinguished by its knowledge of correct ritual essential for preserving the social order. The course examines the changing ways in which knowledge and political power have been mutually implicated in traditional, classical, and modern societies.
PS4233 - Existentialist Political Theory
Units: 5
Pre-requisite: Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS with a minimum CAP of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion: Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module is an in-depth study of Friedrich Nietzsche’s, Jean-Paul Sartre’s and Albert Camus’s political ideas. Reading selections from Nietzsche’s Genealogy of Morals, Thus Spoke Zarathustra and Sartre’s Being and Nothingness, as well as Camus’s The Rebel and Myth of Sisyphus, this module introduces students to the major political ideas, concepts and problems of existentialist philosophy. Among the topics covered will be Kafka and Kierkegaard’s Nietzschean critique of democracy and Camus’s famous break with Sartre over Stalinist-Leninism. This module is for students with a background in political philosophy and an interest in existentialism and democratic theory.
PS4236 - Environmental Political Theory
Units: 5
Pre-requisite: Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS, with a minimum CAP of 3.20 or be on the Honours track, and PS3274.
Preclusion: Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
In this module, we will discover how environmental problems have exceeded their boundary as an “issue area” and have altered contemporary political theorizing. This includes questions related to the roles of the state, the borders of the moral community, and matters of justice. We will trace the transformation of liberal, republican, conservative, socialist, and feminist political thought in the wake of environmental politics. Finally, we will ask whether there is such a thing as a distinctly “green” political theory.
PS4237 - Capitalism and Political Theory
Units: 5
Pre-requisite: Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS modules, with a minimum CAP of 3.20 or be on the Honours track. Completed either PS2258 Introduction to Political Theory or PS2204 Modern Western Political Thought.
Preclusion: Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module investigates the ways in which political philosophers have legitimated, questioned, and critiqued property, markets, money, wage labour, and profit, as well as capitalism as a system. Students will become familiar with liberal, libertarian, Keynesian, Polanyian, and Marxist theories of capitalism and its institutions. In order to understand our contemporary political economy and how it came to be, the module will place particular emphasis on philosophies that justify capitalism and how capitalism has been linked to freedom, equality, justice, and utility.
PS4238 - The Politics of Recognition
Units: 5
Pre-requisite: Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS, with a minimum CAP of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion: Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module examines some of the major debates surrounding the “struggle for recognition” and its relation to the politics of identity and difference. It explores why recognition is an essential human need and how it is foundational to the ways in which we conceive of ourselves and others. It also studies how recognition struggles are often seen as underwriting many contemporary political and social movements, and how they relate to concerns about justice, equality and freedom. Finally, it examines if recognition might, oddly enough, itself become a means of oppression and injustice.
PS4298 - Continental Political Theory: Freedom and the Iron Cage
Units: 4
Pre-requisite: Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS have read and passed PS2204 and PS3232
Preclusion: Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This course analyses twentieth and twenty-first century political and legal thinkers from the "continental" tradition, with a focus on those associated with the Frankfurt School. Frankfurt School seeks human emancipation by striving "to create a world which satisfies the needs and powers of" human beings. To achieve this, its thinkers adopt an interdisciplinary approach, blending politics, law, social theory, economics, and history to diagnose and resolve structural pathologies that undermine freedom. The course traces the dialogue that emerges among these thinkers, demonstrating the arguments and counterarguments for various positions and highlighting why their ideas remain relevant to political theory today.
PS4299 - Theory and Politics of AI
Units: 4
Pre-requisite: Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS
Preclusion: Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This course offers an introduction to the theory and politics of AI. The theory segment locates AI in the context of dreams of creating artificial life and the problem of the definition of intelligence. In examining the genesis of modern computing, it treats the mid-twentieth century as a turning point. It investigates how early failures at developing AI have been addressed via the creation of large language models. The politics component studies some of the contemporary political issues raised by AI, including its economy implications, rising energy and environmental costs, the potential for political deception, and implications for international order.
PS4303/ PS4303HM - Political Theory of Meritocracy
Units: 4 and 5
Pre-requisite: Completed 80 units, including 28 units in PS, with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion: PE4103S/ PE4103SHM
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This is an advanced political theory course investigating the idea, discourse, and practice of meritocracy. First, we will investigate the political theory of meritocracy, specifically the set of discourses that give content to the idea of meritocracy and justify it as an ensemble of social and political practices. Particular attention will be given to legitimations rooted in equality and freedom. Secondly, the course will present political-theoretic critiques of meritocracy, including those of democrats, communitarians, and socialists. Through these criticisms, students will be positioned to critically reflect on meritocracy and weigh it against potential alternatives. Should societies be meritocratic?
PS4322/ PS4322HM - Feminist Theory
Units: 4 and 5
Pre-requisite: Completed 80 units, including 28 units in PS, with a minimum GPA of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion: PS4222
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This course introduces students to the major topics and currents in feminist theory. Through an analysis of both historical and contemporary feminist writings, we will explore the internal diversity within feminist theory in terms of philosophical orientations and practical implications. How do feminist theorists reinterpret the central concepts of political theory such as consent, power, equality of opportunity, justice, agency and victimization? How do they politicize sexuality, motherhood, housework? What are the contentious issues and shared goals among distinct feminist currents? How do they shape the terms, priorities, agendas and strategies of advocacy groups and women’s’ movements?
PS4883 - Topics in Political Theory
Units: 5
Prerequisite(s):
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS with a minimum CAP of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS with a minimum CAP of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module will offer special topics in political theory. Students should check the topics that are on offer in a given semester before enrolling in the appropriate section of the module.
PS4883A - Orientalism and Femininity
Units: 5
Prerequisite(s):
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS with a minimum CAP of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PS, or 28 Units in SC, or 28 Units in GL/GL recognized non-language modules, with a minimum CAP of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): NilThis course explores the construction of an Oriental femininity in western scholarly, journalistic, and artistic production in the 19th and 20th century. It begins by examining colonial representations of Oriental women mapped onto an exotic fantasy of the harem. It then traces the imprint of the Orientalist cosmology upon 20th century portrayals of Muslim women within the context of a “clash of civilizations” and American intervention in Afghanistan. It also addresses the “headscarf controversy” that has erupted in France in the 1980s, and the linkages between the “veil”, agency, Islam, and secular modernity.
PS5201R - Seminar in Political Theory
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): PS5315/PS5315R
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This is a core module in political theory designed for students in any subfield of political science. It selectively examines both the history of the subject and current ideas, theorists, and methodologies. Particular attention is given to alternative understandings of the activity of theorising (e.g., scientific explanation, historical explanation, cultural interpretation, moral prescription, and philosophical analysis of concepts and presuppositions) and to debates about the character and aims of political theorising.
GL4881A - Colonial, Anticolonial and Postcolonial Globalizations
Units: 5
Pre-requisite: Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in GL/GL recognised non-language modules, or 28 Units in SC, or 28 Units in PS, with a minimum CAP of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
This module critically examines key literary, philosophical, and political texts in colonial, anticolonial and postcolonial thought through the lens of contemporary globalization. Themes of universality and particularity, the colonizer/colonized relation, the nature of being human, representation and critique, politics and economics, and different visions of how to live in the world will be addressed by careful engagement with primary and secondary texts. Themes will be examined through broader concerns about patterns of global connection, differentiation and belonging. Self-reflection, analysis and critique will be aimed at connecting colonial, anticolonial and postcolonial thought to globalization and how we live in the world.
PH2202 - Major Political Philosophers
Units: 4
Prerequisite(s): Nil
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module will introduce students to some of the major political philosophers in the Western tradition by examining their different views on such issues as the nature and basis of justice, its relation to equality and liberty, the justification of the state, and the basis of political obligation.
PH4202 - Political Philosophy
Units: 5
Prerequisite(s):
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PH or 28 Units in PS, with a minimum CAP of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PH or 28 Units in PS, with a minimum CAP of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module will discuss some of the central issues in political philosophy such as the basis and limits of toleration and individual liberty, the importance of a shared morality, and the role of the state in meeting the claims of different conceptions of what a worthwhile life should be. In plural societies, with a diversity of different values, what would be a fair basis for social co-operation?
PH4203 - Issues in Moral Philosophy
Units: 5
Prerequisite(s):
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PH or 28 Units in NM, with a minimum CAP of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PH or 28 Units in NM, or 28 Units in PS, with a minimum CAP of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module examines different issues in meta-ethics or normative ethics. It asks questions such as: Can ought be derived from is? Are there natural laws? Is morality about an agent’s character or actions? Are actions morally justified by consequences or compliance with moral laws or principles? It may also examine and assess different schools of moral philosophy, such as utilitarianism, Kantian ethics or virtue ethics, or a current debate among moral philosophers, for example, the nature and role of intuition, or emotions, in acting morally.
PH4205 - Topics in East Asian Philosophy
Units: 5
Prerequisite(s):
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PH, with a minimum CAP of 3.50 or be on the Honours track. PH2301 or PH2302.
Cohort 2012 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PH, or 28 Units in PS, or 28 Units in GL/GL recognised non-language modules, with a minimum CAP of 3.20 or be on the Honours track. PH2301 or PH2302.
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
Specific topics from in East Asian Philosophy (e.g., Chinese, Japanese, Korean) will be discussed in the module. The aim is to introduce students to a more in depth study of traditional East Asian Philosophical texts and issues debated in them. The texts selected will focus on specific topics and traditions and will vary from year to year.
PH4210 - Topics in Western Philosophy
Units: 5
Prerequisite(s):
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PH or 28 Units in EU/LA (French/ German)/recognised modules, with a minimum CAP of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012 - 2014 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PH, or 28 Units in PS, or 28 Units in EU/LA (French/German)/ recognised modules, with a minimum CAP of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2015 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PH, or 28 Units in PS, or 28 Units in EU/LA (French/German/ Spanish)/recognised modules, with a minimum CAP of 3.20
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module deals with specific topics of current interest and controversy in Western philosophy. The topics to be discussed may be in, but are not limited to, philosophy of science, philosophy of language, philosophy of psychology, epistemology, metaphysics, ethics, or social and political philosophy.
PH4262 - Nietzsche
Units: 5
Prerequisite(s):
Cohort 2011 and before:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PH or 28 Units in EU/LA (French/ German)/recognised modules, with a minimum CAP of 3.50 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2012 - 2014 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PH, or 28 Units in PS, or 28 Units in EU/LA (French/ German)/ recognised modules, with a minimum CAP of 3.20 or be on the Honours track.
Cohort 2015 onwards:
Completed 80 Units, including 28 Units in PH, or 28 Units in PS, or 28 Units in EU/LA (French/German/Spanish)/recognised modules, with a minimum CAP of 3.20 or be on the Honours track
Preclusion(s): Nil
Cross-listing(s): Nil
This module will focus on the philosophy of the 19th Century German philosopher Friedrich Nietzsche. It will proceed chronologically through Nietzsche's most significant writings, such as The Gay Science; Thus Spoke Zarathustra; Beyond Good and Evil; On the Genealogy of Morality. Most of the attention will be on primary sources. All materials will be in English.

